---
title: AI Tooling
description: Tools to help you use Nirvana Labs documentation with AI assistants and LLMs.
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/ai-tooling/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/ai-tooling/index.md
---
## llms.txt
Nirvana Labs provides machine-readable documentation formats for AI integration:
- [`llms.txt`](/llms.txt) - A lightweight index of all documentation pages with titles and URLs
- [`llms-full.txt`](/llms-full.txt) - Full documentation content in a single file, optimized for LLM context windows
Per-category documentation files are also available for more focused context:
- [`cloud/llms-full.txt`](/cloud/llms-full.txt) - Cloud Infrastructure documentation only
- [`blockchain/llms-full.txt`](/blockchain/llms-full.txt) - Blockchain/RPC documentation only
- [`sdks/llms-full.txt`](/sdks/llms-full.txt) - SDK documentation only
You can also append `/index.md` to any documentation page URL to get the raw Markdown content. For example:
- HTML: `https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/introduction/`
- Markdown: `https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/introduction/index.md`
Additionally, there is a **Copy page** button in the top right corner of every page that allows you to copy the current page as Markdown to give to your LLM of choice.
## MCP
Nirvana Labs provides an MCP (Model Context Protocol) server that enables AI assistants to interact with the Nirvana Labs API directly.
### Installation
#### Direct invocation
You can run the MCP Server directly via `npx`:
```sh
export NIRVANA_LABS_API_KEY="My API Key"
npx -y @nirvana-labs/nirvana-mcp@latest
```
#### Via MCP Client
For clients with a configuration JSON, add the following to your MCP configuration:
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"nirvana_labs_api": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@nirvana-labs/nirvana-mcp"],
"env": {
"NIRVANA_LABS_API_KEY": "My API Key"
}
}
}
}
```
#### Cursor
Install the MCP server in Cursor using the button below. Set your environment variables in Cursor's `mcp.json` (Cursor Settings > Tools & MCP > New MCP Server).
[](https://cursor.com/en-US/install-mcp?name=%40nirvana-labs%2Fnirvana-mcp&config=eyJjb21tYW5kIjoibnB4IiwiYXJncyI6WyIteSIsIkBuaXJ2YW5hLWxhYnMvbmlydmFuYS1tY3AiXSwiZW52Ijp7Ik5JUlZBTkFfTEFCU19BUElfS0VZIjoiU2V0IHlvdXIgTklSVkFOQV9MQUJTX0FQSV9LRVkgaGVyZS4ifX0)
#### VS Code
Install the MCP server in VS Code by clicking the link below. Set your environment variables in VS Code's `mcp.json` (Command Palette > MCP: Open User Configuration).
[Install in VS Code](https://vscode.stainless.com/mcp/%7B%22name%22%3A%22%40nirvana-labs%2Fnirvana-mcp%22%2C%22command%22%3A%22npx%22%2C%22args%22%3A%5B%22-y%22%2C%22%40nirvana-labs%2Fnirvana-mcp%22%5D%2C%22env%22%3A%7B%22NIRVANA_LABS_API_KEY%22%3A%22Set%20your%20NIRVANA_LABS_API_KEY%20here.%22%7D%7D)
#### Claude Code
Install the MCP server in Claude Code by running the following command in your terminal:
```sh
claude mcp add nirvana_labs_api --env NIRVANA_LABS_API_KEY="Your API Key" -- npx -y @nirvana-labs/nirvana-mcp
```
### More Information
For more details about the MCP server, see the [npm package](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@nirvana-labs/nirvana-mcp) or the [GitHub repository](https://github.com/nirvana-labs/nirvana-typescript/tree/main/packages/mcp-server).
---
title: Overview
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/index.md
---
## What are RPC Nodes
RPCs (Remote Procedure Call) are a set of protocols and interfaces that allow communication with remote servers to execute programs in a separate location. They provide a way for developers and their applications to retrieve data from blockchains and execute code on remote decentralized servers, known as nodes. When developers create decentralized applications (dApps) that connect to RPCs, these dApps can respond to users' requests for blockchain-related information and perform actions like cryptocurrency transactions.
When users interact with a dApp to carry out transactions, their requests travel through a RPC to connect with the nodes housing blockchain data. This data is then forwarded to the mempool, where it waits to be processed by validator nodes and added to the blockchain.
## RPC Use Cases
Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs) underpin multiple functionalities in the blockchain ecosystem. They are commonly used for:
* **Retrieving Data**: Decentralized applications use RPCs to fetch data from the blockchain network. For instance, a blockchain explorer application can employ RPC to inquire about transaction specifics, verify account balances, or extract information concerning specific blocks. This data retrieval capability remains crucial for building wallets, analytical tools, and other services reliant on blockchain.
* **Executing Transactions**: RPCs allow applications to initiate and carry out transactions on the blockchain network. A decentralized exchange platform, for instance, uses RPCs to dispatch transaction details, encompassing the sender's address, the recipient's address, and the transfer amount. Subsequently, RPCs facilitate the transaction verification and confirmation process, ensuring its integration into the blockchain.
* **Interacting with Smart Contracts**: RPCs play a pivotal role in engaging with smart contracts on the blockchain. Applications can invoke functions within smart contracts through an RPC, supplying the requisite parameters and recovering the resultant data. This empowers developers to construct decentralized applications (dApps) capitalizing on smart contracts' programmable and self-executing capabilities.
* **Monitoring and Managing Blockchains**: RPCs provide a suite of tools for monitoring and managing blockchain nodes. Applications can employ RPC commands to acquire insights into the network, such as the count of connected peers, synchronization status, or mining difficulty. This data is valuable for network analysis, performance oversight, and maintenance objectives.
* **Facilitating Cross-Chain Interactions**: RPCs streamline cross-chain interactions and enhance interoperability. By leveraging RPCs, applications can communicate with nodes across diverse blockchain networks, enabling data exchange or transaction execution spanning multiple chains. This capacity to interface with many blockchains promotes the development of decentralized applications that harness the combined capabilities of various networks.
## Archive vs Full Nodes
There are typically two different types of nodes that one can run for any specific blockchain network, a full node and an archive node.
### Archive Nodes
Archive nodes contain the full block history from genesis to the current state for a specific blockchain ledger. They are used by dApps that need the ability to retrieve data for any time period of the blockchain's history.
### Full Nodes
Full nodes typically have settings enabled that prune away data older than a specific number of blocks to save disk space. These nodes do not store all state data back to the Genesis block but all state data can be retrieved from local storage or a snapshot if needed. Full nodes are used for reading or writing data in a “live” time period.
## Flex vs Dedicated Nodes
### Flex Nodes
We call our global RPC network our “flex nodes” because every API request is geo-load balanced across all our data center locations. This is important because each API request will automatically be routed to the nearest data center location that can provide the lowest latency response, making those calls flexible or “flex.”
This is our most common product offering that anyone and everyone can use. This includes individuals looking to change their wallet RPC to enterprises with millions of daily active users and significant request volume. Our global RPC network provides the lowest latency requests possible while offering near-perfect uptime.
### Dedicated Nodes
Dedicated nodes are an alternative to our flex nodes and are available to all customers. Dedicated nodes are single nodes with dedicated compute resources deployed in a specific data center location for a specific customer’s utilization. This means individual nodes are not load-balanced by default, but we can load-balance multiple dedicated nodes for you.
Dedicated nodes have dedicated compute resources that are customizable to your needs. There are no request limitations on these dedicated nodes. However, there are compute and memory limitations based on your node’s resources. Heavier compute requests such as debug\_traceCall will utilize more compute than an eth\_blocknumber request. If you’re doing a lot of transaction volume or heavy compute requests, increasing the size of your dedicated node is recommended to avoid any degraded performance.
---
title: Account Management
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/account-management/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/account-management/index.md
---
## Dashboard
To open the **Dashboard** panel, follow these steps:
1. Sign in to Nirvana Labs with your username and password.
2. Click on **Dashboard** in the top right corner of the homepage to open the corresponding panel.
> 👍 You can now see the API Request and Nodes statistics in your **[Dashboard](https://www.nirvanalabs.io/dashboard/nodes)**.
In the Dashboard, you can monitor and carry out the following functions:
### Create a Node
- Deploys a new node to the blockchain network of your choosing.
### Overview
- Provides a high-level summary of your RPC node analytics, offering a quick snapshot of crucial statistics and node management capabilities.
### API Request Statistics:
| | |
| :--------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| **Total** | The number of API requests made through an RPC node. |
| **Success Rate** | The rate of successful API requests, indicating the reliability of an RPC node. |
| **Successful** | The count of API requests that were successfully executed. |
| **Failed** | The count of API requests encountering errors or issues. |
| **Unauthorized** | The number of API requests denied due to lack of authorization. |
| **Rate Limited** | The number of API requests subjected to rate limiting |
### Nodes
- Create, manage, and delete RPC nodes. After running a node, it displays detailed information about each node in a tabular format:
| | |
| :------------- | :----------------------------------------------------- |
| **Name** | The user-assigned name for the RPC node. |
| **Blockchain** | The blockchain network associated with the node. |
| **Network** | Specifies the network configuration of the node. |
| **Type** | Indicates the node type, such as "Flex" or "Dedicated" |
| **Status** | Displays whether the node is running or not. |
| **Created On** | The date when the node was initially set up. |
### Reports
| | |
| :------------------------ | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **Request Rate** | measures the number of incoming requests to the RPC node. The sampling interval for this metric is set to 1 second. |
| **Latency and Bandwidth** | provides insights into the latency and bandwidth performance of your RPC nodes, helping you assess the efficiency of your infrastructure. |
| **RPC Log Data** | gives detailed logs and data related to RPC requests made through your nodes, facilitating troubleshooting and analysis of API interactions. |
---
title: How to Manage Your Account
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/account-management/how-to-manage-your-account/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/account-management/how-to-manage-your-account/index.md
---
## Billing
You usually start on Nirvans Labs as a Free Plan user and to do so you need to open an account with your email address on [https://www.nirvanalabs.io](https://www.nirvanalabs.io/).
Once you register, you gain access to the Dashboard and the available Plans where you can start with our Free Plan or a paid plan.
You can head to the [pricing](https://www.nirvanalabs.io/dashboard/billing) page and click on [Compare Plans](https://www.nirvanalabs.io/pricing) for a side-by-side comparison of the performance features and rate limits supported depending on the selected plan.
## How to upgrade or downgrade your plan
The managed RPC services come with both Free and Paid service plans but differ significantly in rate throughput, request rates and other performance metrics depending on the plan selected.
You can change the current plan you're on at any time by visiting the [Billing](https://www.nirvanalabs.io/dashboard/billing) tab in your Dashboard.
You then click the 'Select Plan' button of the plan you want to switch to.
## Enabling Overage Requests
If you want to stay on your current plan but continue sending API requests after reaching your monthly limit, you can enable overages.
To do so, click on the sliding button in the top right corner opposite the Overage Requests and it will be activated.
## How to change the billing method
Nirvana Labs supports various billing methods for accessing the paid managed RPC services. You can access them from the [Payment Preferences](https://www.nirvanalabs.io/dashboard/billing#payment-preferences) tab in the Billing section of the Dashboard.
Click on Add Payment Method and fill out the information for your preferred method.
### Billing methods accepted
Nirvana Labs supports crypto and bank transfers for annual subscriptions. We will be adding crypto support for monthly payments soon.
---
title: Security
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/account-management/security/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/account-management/security/index.md
---
Nirvana Labs uses a combination of tools and mechanisms to secure network endpoints and users' API keys.
## API Keys
Nirvana Labs uses an API Key in URL (Path Parameter) to authenticate API requests. The API key is directly embedded in the request's URL and point to a specific REST API resource. An example of a URL-based API request is:
```
curl -X POST https://eth-mainnet.g.nirvanalabs.io/v2/demo \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"eth_blockNumber","params":[],"id":1}'
```
### Share API key access
Team account holders can share access to their Nirvana Labs API keys with other account members.
To share an API key:
1. In the Dashboard, select the API that you want to share.
2. Select the API Key Sharing tab.
3. If you haven't shared the API key yet, select Invite Members.
4. Type one or more user emails, assign the user role, and select Share API Key.
5. Select Confirm.
### Creating a new API key
To create a new API key, go to the Security tab in your Dashboard and click on the Refresh button next to your current API key.
A pop-up window will notify you that you are about to generate a new API key to replace the existing one. Click on Confirm to continue.
The new API key will overwrite the previous one and will be used by Nirvana Labs to authenticate all your API requests.
### User roles
**Administrator**
The Nirvana Labs account owner who created the API key.\*
* Can change roles, and revoke and resend invites.
* Can edit security settings and view API key statistics.
* Can delete the API key.
* View billing details.
*\*Ownership of an API key cannot be changed once created.*
**Developer**
* Has access to the API key name, security settings, and collaborator list.
* Can edit security settings and view API key statistics.
* Can delete the API key.
* View billing details.
#### Accept an invitation
You'll receive an email invitation to access an API key. In the email invitation, select Confirm and accept the invitation.
You can view all keys that you own, and all keys shared with you, by selecting Key Sharing in the Dashboard.
---
title: Team vs Individual Accounts
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/account-management/team-vs-individual-accounts/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/account-management/team-vs-individual-accounts/index.md
---
Nirvana Labs' managed RPC services support Team and Individual accounts to cater to the diverse needs of users and companies.
## Individual Account
| | |
| :---------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| **Sign-Up Requirement** | Users must initially create an individual account to access our services. |
| **API Keys** | Users are assigned a unique API key to interact with Nirvana Labs' RPC nodes and services. That API Key is a token required for interacting with the service and making API requests. |
## Team Account
| | |
| :------------------ | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **Setup** | Once you have an individual account, you can create a Team or be invited to join an existing Team. |
| **API Key Sharing** | Teams operate with a shared API key, which is utilized collectively by all team members for interaction with our RPC nodes and services. |
### Roles within Team Accounts
| | |
| :---------------- | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **Developer** | Users with a "Developer" role have general access to the team's resources, such as RPC nodes and related analytics. Developers can manage API keys. |
| **Administrator** | Administrators have enhanced privileges in addition to the developer privileges, enabling them to invite or remove users from the team and manage billing information associated with the team's account. |
This setup ensures a flexible and collaborative user environment, allowing efficient RPC node access management while maintaining the necessary control and security measures via designated roles within Team accounts.
---
title: Authentication
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/authentication/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/authentication/index.md
---
After you create a node from the Dashboard and give it a name, the system will generate a unique API key attached to that node. This API is required for interacting with the service and making API requests. It will appear at the top of your Dashboard in the following format:
```
https://polygon.nirvanalabs.xyz/polynode?apikey=0c4d6970326cf823e9d59504b2679f361131
```
where the string of characters following "apikey=" is the API key for the node.
You can create several nodes if needed and the system will generate the endpoint URL. Endpoints are created with the API key and node name which the user specifies on creation. Your requests cannot be processed without the API key, and you will receive a 400 Bad Request error.
The Nirvana CDN authenticates the request through the API key when you copy the endpoint URL from the project Dashboard and paste it into the header of the query params in the API platform of your choice.
Each node has its own methods for interacting with the blockchain network. You can find the methods for the nodes Nirvana Labs supports in the Networks section in the tech docs.
---
title: FAQ
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/faq/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/faq/index.md
---
## What are RPC URLs & APIs?
For a software application to interact with a specific blockchain - either by reading blockchain data or sending transactions to the network - it must connect to a blockchain node. For this purpose, most blockchains implement a JSON-RPC specification, so applications can rely on a uniform set of methods regardless of the specific node or client implementation. JSON-RPC is a stateless, light-weight remote procedure call (RPC) protocol. It defines several data structures and the rules around their processing. It is transport agnostic in that the concepts can be used within the same process, over sockets, over HTTP, or in many various message passing environments. It uses JSON (RFC 4627) as data format.
## What is an API Key?
API keys ensure secure authentication and authorization processes between users and blockchains. They are instrumental in verifying user identity, controlling access to sensitive data, and monitoring API activity.
An API key is a distinctive string of randomly generated characters or a set of unique codes that serve as authentication credentials for clients to access an API. By utilizing API keys to query or access blockchains, you can establish a robust framework that allows only authorized requests to interact with the API, safeguarding sensitive data and mitigating the risk of misuse.
API keys serve as a unique identifier to facilitate the interaction between users and blockchains. They verify the user's identity and grant them access to specific information or privileges to perform designated actions. This mechanism guarantees that only authorized individuals can engage with the blockchain or exchange platform, reinforcing security and integrity.
You can obtain an API key for free to try Nirvana Labs' managed RPC services under certain limitations, and we have several premium plans. Please check out the [rates and plans](https://nirvanalabs.io/pricing).
By following a few [simple steps](/nodes/account-management/), you can easily get an API key and start interacting with the desired network RPC nodes by utilizing the Ethereum RPC endpoint, Polygon RPC endpoint, Arbitrum RPC endpoint and Avalanche RPC endpoint Nirvana Labs supports.
## Which API Does Ethereum Use?
Ethereum operates on the JSON-RPC API standard. The Ethereum JSON-RPC API serves as the fundamental framework for the Ethereum network, facilitating all types of blockchain interactions. This comprehensive suite of APIs empowers users to access many functionalities, including reading block and transaction data, querying chain information, executing smart contracts, and storing data on the blockchain.
## How Does Nirvana Labs's API Work?
The Nirvana Labs API empowers developers and users by allowing them to read and write data on the blockchain.
If you're not familiar with the inner workings of a blockchain, here's a brief overview:
> 📘 Blockchains consist of interconnected blocks of data.
> 📘 These blocks are stored across distributed nodes.
> 📘 Each node fulfils the role of a "mini-server" that enables its operator to interact with and manipulate blocks of data.
Through Nirvana Labs' API, developers access a high-level infrastructure that facilitates seamless interaction with the respective network. With API integration, Nirvana Labs developers can effortlessly send read and write requests to the blockchain.
At Nirvana Labs, we handle the complex underlying processes so that developers can dedicate their attention to building innovative products and applications. We strive to simplify the development experience, allowing our users to focus on realizing their ideas without getting bogged down by technical intricacies.
## What Methods Does Nirvana Labs Support?
Nirvana Labs supports the full list of JSON-RPC API methods as listed in the [JSON-RPC specification](https://github.com/ethereum/execution-apis).
## What is an API Endpoint?
When making an API call, you need to specify the endpoint, which is a URL consisting of the address and name of the node, along with the specific path for the desired endpoint.
The base URL format is as follows:
```
https://[blockchain name].nirvanalabs.xyz/[node name]?apikey=[xxxxxx]
```
where
* The node-name corresponds to the name you've given to the node you've created for the specific blockchain.
* The API key is the private API key generated by Nirvana Labs that gives you access to the node.
You then use the custom URL generated for that node to access and query the blockchain via an additional layer of CDN and an API gateway.
---
title: RPC Requests
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/rpc-requests/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/blockchain/rpc-nodes/rpc-requests/index.md
---
Nirvana Labs Nodes support various open-source libraries for sending and receiving Ethereum data. We believe in supporting and contributing towards these open-source libraries to build transparency within web3 and eliminate a single point of reliance on one library.
Nirvana Labs operates RPC endpoints that can be accessed using cURL, JavaScript, Python, Ruby, and any relevant Web3 SDKs. Nirvana Labs supports a wide range of Ethereum APIs, including:
### EthersJS
The ethers.js library aims to be a complete and compact library for interacting with the Ethereum Blockchain and its ecosystem. It was initially designed for use with ethers.io and has since expanded into a more general-purpose library.
To use it, you can install it by running:
```
npm install --save ethers
```
[EthersJS Documentation](https://docs.ethers.io/v5/)
### Web3.Py
Web3.py is a Python library for interacting with Ethereum. It's commonly found in decentralized apps (dapps) to help with sending transactions, interacting with smart contracts, reading block data, and various other use cases. The original API was derived from the Web3.js Javascript API, but has since evolved toward the needs and creature comforts of Python developers.
You can install the Python library for interacting with Ethereum by running:
```
pip install web3
```
[Web3.Py Documentation](https://web3py.readthedocs.io/en/v5/)
### Eth.Rb
A straightforward library to build, sign, and broadcast Ethereum transactions. It allows the separation of key and node management. Sign transactions and handle keys anywhere you can run Ruby and broadcast transactions through any local or remote node. Sign messages and recover signatures for authentication.
Install it by running:
```
gem install eth
```
[Eth.Rb Documentation](https://github.com/q9f/eth.rb)
### cURL
Most \*nix based systems support cURL - a command line tool and library for transferring data with URLs. Check if you have it by running the following command:
```
curl -h
```
[cURL Documentation](https://curl.se/docs/manpage.html)
### WebSocket cat (wscat)
WebSocket cat (wscat) is a convenient tool for connecting to WebSocket APIs in your terminal. Install it using the following command:
```
npm install -g wscat
```
You can connect to the Ethereum node with wscat using two options. Run:
```
wscat -c 'wss://eth.getblock.io/mainnet/' --header 'x-api-key: '
```
or
```
wscat -c 'wss://eth.getblock.io/mainnet/?api_key='
```
When the command is performed, you will get a response that the connection is successfully enabled inside the terminal.
[Wscat Documentation](https://github.com/websockets/wscat)
---
title: Virtual Machines (VMs)
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/vms/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/vms/index.md
---
Virtual Machines (VMs) serve as the backbone of Nirvana Cloud, offering high-level performance and flexibility required to run a wide array of applications and workloads. Capitalising on our hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI), Nirvana Cloud's VMs are designed to operate on bare metal servers, thereby providing an abstraction layer that separates the user's applications from the underlying hardware.
## Features
### Creation and Management
Nirvana Cloud allows users to create and manage VMs effortlessly using its intuitive dashboard interface. These VMs impersonate hardware conditions and operate independently from the underlying physical machinery.
### Resource Allocation
Nirvana Cloud guarantees unhindered access to crucial resources such as compute, memory, storage, and networking for the VMs. These allocations can be adjusted based on the unique requirements of different applications.
### CPU & RAM Performance
Thanks to its ability to bypass unnecessary virtualization latencies and provide direct hardware access, Nirvana Cloud ensures top-notch performance from its VMs. This performance, marked by reduced latency and limited resource contention, is ideal for resource-intensive workloads such as data analytics, machine learning, and high-performance databases.
### Instance Customization
VMs in Nirvana Cloud can be customized to the user's needs, with the ability to modify key attributes such as CPU cores, memory, storage volume, and network configurations. This level of customization provides users with the opportunity to fine-tune their VMs to suit specific operational needs.
### VM Security & Isolation
Nirvana Cloud VMs operate in isolation from each other, providing robust security and privacy. Users gain full access to the VM's entire operating system and any user processes occur exclusively within the VM. Nirvana Cloud's tasks run beneath the VM layer, within the hypervisor. This setup, combined with robust network protocols, bolsters security and protects critical data and applications.
Nirvana Cloud's VMs are versatile and cater to a broad range of use cases across on-premises and cloud environments. Setting up a VM is a straightforward process—simply follow Nirvana Cloud's setup guide to get started.
---
title: CPU and Memory
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/vms/cpu-and-ram/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/vms/cpu-and-ram/index.md
---
Nirvana Cloud supports VMs using any combination of CPU, RAM, and storage. You are not limited to preset sizing options, allowing you to design virtual machines that align precisely with your application requirements. By adjusting the compute, memory, and storage sliders, you can easily customize the size of your virtual machine.
| | |
| :----------------------- | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **Unique Configuration** | Fully customizable VM sizes, ensuring each VM is tailored to individual project requirements. |
| **User Interface** | Users can effortlessly adjust compute, memory, and storage parameters using intuitive sliders, providing a user-friendly experience. |
| **Efficient Scaling** | As your project grows or needs change, seamlessly alter configurations without complex migrations or setups. |
| **Optimization** | By tailoring resources precisely to requirements, you can eliminate wastage and ensure cost-effectiveness, maximizing your return on investment. |
# E7 VM Specs
## CPU Type and Specs
Nirvana Cloud utilizes the AMD EPYC 7513 chipset for its bare metal servers, offering impressive performance capabilities. The CPUs operate at clock speeds of up to 3.65 GHz, ensuring rapid data processing and application responsiveness. AMD EPYC 7513 is a server/workstation processor with 32 cores, operating at 2.6 GHz by default. The use of AMD Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) effectively doubles the core-count to 64 threads for superior performance in various workloads, making it a top choice for diverse computing tasks.
## RAM Type and Specs
Nirvana Cloud is specifically tailored for applications, such as blockchain data indexers and DeFi platforms, that demand significant RAM capacities for optimal performance. With the E7 virtual machines powered by the AMD EPYC 7003 series chipset, users benefit from efficient RAM utilization tailored for Web3 workloads. Nirvana Cloud's adaptive scalability allows users to seamlessly transition between different RAM configurations - from 8 GBs to 224 GBs - without the hassle of over-provisioning. Additionally, users can easily adjust RAM allocations directly from the VM details page, streamlining optimization and ensuring peak performance.
---
title: FAQ
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/vms/faq/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/vms/faq/index.md
---
---
title: Monitoring
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/vms/monitoring/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/vms/monitoring/index.md
---
## Performance and Utilization Metrics
When viewing the details of your virtual machine, you can access comprehensive performance and utilization metrics. This includes CPU utilization, RAM utilization, storage utilization, bandwidth ingress, and egress. Monitoring these metrics provides valuable insights into resource utilization and aids in optimizing the performance of your applications.
Nirvana Cloud provides visibility into the associated resources of your virtual machine. You can identify the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and storage volumes linked to your VM. You can obtain in-depth information about these resources by accessing the VPC or storage volume details, facilitating efficient navigation and management within the Nirvana Cloud platform.
Note: For more detailed technical documentation and instructions, refer to the official Nirvana Cloud documentation, which provides step-by-step guidance on deploying and managing virtual machines.
## BTOP
BTOP is a feature-rich and high-performance system monitoring tool that offers users a real-time glimpse into various system metrics, including CPU, memory, and network statistics. With its intuitive and visually appealing interface, users can effortlessly navigate and drill down into detailed statistics, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of their system's performance.
BTOP comes pre-installed on Nirvana Cloud VMs, allowing users to start monitoring without any additional setup. For those looking to dive deeper into its capabilities or seeking updates, the official repository is readily available at BTOP on GitHub.
---
title: OS Images
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/vms/os-images/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/vms/os-images/index.md
---
Nirvana Cloud currently supports Linux Ubuntu for server creation, ensuring seamless integration and deployment. Recognized as the most popular OS choices within Web2 and Web3, they guarantee stability and robust performance for diverse applications.
For the latest versions, please visit the [Dashboard](https://dashboard.nirvanalabs.io) or query the [API](https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/api/resources/compute/subresources/vms/subresources/os_images/methods/list/).
---
title: Volumes
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/volumes/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/volumes/index.md
---
## Boot Volumes
Nirvana storage volumes are engineered to deliver significantly higher performance than similar elastic block storage solutions. The boot volume forms the foundation of the operating system in your Virtual Machine. It is a dedicated storage unit where the bootable operating system, system files, and data needed during the system start-up process are stored. Just like a physical computer's hard drive stores the essential files, the boot volume serves the same purpose in a VM.
Nirvana Cloud's boot volumes are designed to handle high-intensity input/output operations and deliver superior performance. It ensures that even demanding applications boot up effortlessly and function smoothly.
## Data Volumes
Beyond the boot volume, a VM's storage capacity can be expanded by utilizing multiple data volumes.
Depending on the VM's operational needs, multiple data volumes can be added to or removed from a VM in order to increase or decrease the amount of storage.
## Common Use Cases for Multi-Volume Deployments
* Separating the boot volume from the data volume for better performance and easier management.
* Adding additional volumes to a VM for more storage space.
* Utilizing raid configurations for better performance and redundancy.
* Creating separate volumes for different applications or services running on the VM.
* Storing blockchain snapshots temporarily on a second volume and removing that volume after the snapshot extraction is complete.
## Things to Keep in Mind
* Volumes can only be expanded, not shrunk. Make sure to back up any important data before expanding a volume to avoid data loss.
* When adding or removing a volume from a VM, the VM will be stopped while the volume is being added or removed and will be started again once the add/remove operation is complete.
* Make sure to unmount the volume and update the fstab file before removing a volume to avoid boot issues.
* After expanding a volume, make sure to resize the filesystem on the volume to make use of the additional space.
---
title: FAQ
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/volumes/faq/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/volumes/faq/index.md
---
---
title: Accelerated Block Storage (ABS)
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/volumes/storage-types/abs/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/volumes/storage-types/abs/index.md
---
Accelerated Block Storage (ABS) is a high-performance, crypto-tuned block storage layer built for always-hot blockchain data with sustained IOPS, delivering high throughput, high availability, and cost-effective storage for I/O-intensive workloads.
ABS combines cloud elasticity with bare-metal performance, staying fast under sustained load without throttling, burst credits, or surprise bills.
## Overview
Traditional cloud storage was designed for spiky, bursty workloads. Blockchain workloads are different: blocks keep coming, generating continuous I/O for hours or days. Indexers, archives, and trace-heavy nodes stay hot under constant load with no recovery window.
ABS is engineered to stay fast under continuous load. It delivers sustained IOPS indefinitely without time-based throttling, performance cliffs, or gradual degradation.
## Availability
ABS is currently available in the **us-sva-2 (Silicon Valley)** region and being rolled out to all new regions.
## Performance Specifications
| | |
| :--------------------------- | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **IOPS** | 20K baseline (guaranteed) with up to 600K burst capacity |
| **Latency** | Sub-millisecond (~0.3 to 1.5 ms) |
| **Throughput** | Up to 1.6 GB/s writes, 260-380 MB/s sustained, ~600 MB/s reads |
| **Volume Size** | 32 GB to 4 PB |
| **Queue Depth** | Near zero under sustained load |
## Key Features
| | |
| :--------------------------------- | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **Sustained Performance** | No throttling after 2-3 hours like traditional cloud. Stays fast as long as your workload stays hot. |
| **High Availability** | Persistent shared volumes decoupled from compute. Data is never tied to a specific server. If a machine fails, workloads migrate instantly without rebuilds or data loss. |
| **Elastic Scale** | Scale from 32 GB to 4 PB with zero downtime. No hardware changes or re-provisioning required. |
| **Predictable Pricing** | Flat, TB-based pricing ($93.5/TB) with IOPS and throughput included. No burst credits, no metering. |
| **Node-Level Colocation** | Tightest physical data path when paired with Nirvana bare-metal compute for ultra-low latency. |
## Cost Comparison
ABS delivers significant cost savings compared to traditional cloud storage:
* **20x faster than gp3** and 60%+ cheaper
* **1.5x faster than io2** and 80%+ cheaper
## Use Cases
ABS is purpose-built for workloads that require sustained I/O performance:
* **RPC Nodes**: Archive and trace-heavy nodes that stay hot under constant load
* **Indexers**: Continuous indexing workloads with heavy write patterns
* **Databases**: ClickHouse, Postgres, and OpenSearch clusters requiring consistent performance
* **MPC Engines**: Multi-party computation workloads with deterministic latency requirements
* **Rollups**: High-throughput rollup infrastructure
* **Observability & Analytics**: Data-intensive pipelines and ETL workloads
* **Multi-Chain Data Platforms**: Large archives and multi-chain datasets
## Getting Started
ABS is available today for teams running I/O-intensive workloads. [Contact us](https://nirvanalabs.io/contact) to start a POC.
## Known Issues
Expanding Volumes
Currently, after creating an ABS Volume (via VM creation or independently) it cannot be expanded automatically. The Volume will expand but it won't be registered in the OS correctly and thus the additional space will not be immediately usable.
As a temporary workaround, please reach out to the Nirvana team in Slack and we will carry out the Volume expansion.
## FAQ
What is Nirvana ABS?
ABS is Accelerated Block Storage. Our high-ops, low-latency block storage solution available in our generation 2 data center region `us-sva-2`.
Does `us-sva-2` support only ABS?
Yes - `us-sva-2` **only** supports our new Nirvana ABS Block Storage. We may in future introduce more options but for now only ABS is supported for both `boot` and `data` volumes.
Which regions is ABS available in?
ABS will be rolled out and available in all next-generation sites in the coming months.
What is the maximum size of a volume for Nirvana ABS?
ABS can support volumes up to 4 PB. Today customers can provision up to 100 TB automatically and should reach out to the Nirvana team if they want to provision larger volumes.
How do I use Nirvana ABS with the Terraform Provider?
Using the [Nirvana Terraform Provider](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/nirvana-labs/nirvana/latest), set the volume type to `abs`.
For separately managed `nirvana_compute_volume` resources:
```hcl
resource "nirvana_compute_volume" "example_compute_volume" {
name = "my-data-volume"
type = "abs"
size = 100
vm_id = nirvana_compute_vm.id
}
```
For `nirvana_compute_vm` with nested `boot_volume` and `data_volumes` fields:
```hcl
resource "nirvana_compute_vm" "vm" {
region = var.region
name = "my-vm"
os_image_name = data.nirvana_compute_vm_os_images.vm_os_images.items[0].name
ssh_key = {
public_key = var.ssh_public_key
}
cpu_config = {
vcpu = var.cpu
}
memory_config = {
size = var.memory
}
boot_volume = {
size = var.boot_disk_size
type = "abs"
}
data_volumes = [
{
name = "my-data-volume"
size = var.data_disk_size
type = "abs"
}
]
subnet_id = nirvana_networking_vpc.vpc.subnet.id
public_ip_enabled = true
tags = var.tags
}
```
What filesystems work best with Nirvana ABS?
All filesystems work with ABS but we recommend avoiding those with compression as this is handled at hardware level and may introduce additional latencies.
---
title: Local NVMe
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/volumes/storage-types/local-nvme/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/compute/volumes/storage-types/local-nvme/index.md
---
Local NVMe storage is directly attached to your VM, delivering the highest possible performance for workloads that benefit from physical proximity to compute.
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a communications interface and driver that leverages the high bandwidth of PCIe. Crafted to elevate performance, efficiency, and interoperability, NVMe is the industry standard for SSDs.
## Overview
Local NVMe drives are physically attached to the host machine, providing direct access without network overhead. This architecture delivers the lowest possible latency and highest throughput for I/O-intensive workloads.
Unlike network-attached storage, Local NVMe storage is ephemeral and tied to the physical host. If the VM is stopped or the host fails, data on local NVMe drives may be lost. For persistent storage needs, consider [Accelerated Block Storage (ABS)](/cloud/compute/volumes/storage-types/abs).
## Availability
Local NVMe is available in the following regions:
- us-sea-1 (Seattle)
- us-sva-1 (Silicon Valley)
- us-chi-1 (Chicago)
- us-wdc-1 (Washington DC)
- eu-frk-1 (Frankfurt)
- ap-sin-1 (Singapore)
- ap-seo-1 (Seoul)
- ap-tyo-1 (Tokyo)
## Key Features
| | |
| :--------------------------------- | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **Lowest Latency** | Direct PCIe connection to the CPU eliminates network hops, delivering sub-100 microsecond latency. |
| **Maximum Throughput** | NVMe-based block storage can reach a theoretical maximum speed of 1,000,000 IOPS. |
| **Cost-Efficiency** | Nirvana's NVMe-based block storage balances speed and cost, providing a significant performance boost and up to 100x lower costs. |
| **Flexibility and Compatibility** | NVMe drives are compatible with all major operating systems, and their direct communication with the system CPU ensures rapid speeds. |
## Use Cases
Local NVMe is ideal for workloads that prioritize performance over persistence:
* **Boot Volumes**: Fast startup times for VMs
* **Scratch Space**: Temporary storage for data processing and computation
* **Caching Layers**: High-speed cache for frequently accessed data
* **Workloads with External Persistence**: Applications that replicate data to external storage or other nodes
* **Low-Latency Applications**: Workloads requiring the absolute lowest possible latency
## FAQ
Is Local NVMe data persistent?
Yes, however, storage is tied to the physical host, so if the host fails, data on local NVMe drives may be lost. For highly available persistent storage, use [Accelerated Block Storage (ABS)](/cloud/compute/volumes/storage-types/abs).
When should I use Local NVMe vs ABS?
Use **Local NVMe** when you need the absolute lowest latency and highest throughput, and your application can tolerate data loss (e.g., caching, scratch space, or workloads with external replication).
Use **ABS** when you need persistent, highly available storage that survives VM restarts and host failures.
Which regions support Local NVMe?
Local NVMe is available in: us-sea-1, us-sva-1, us-chi-1, us-wdc-1, eu-frk-1, ap-sin-1, ap-seo-1, and ap-tyo-1.
How do I use Local NVMe with the Terraform Provider?
Using the [Nirvana Terraform Provider](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/nirvana-labs/nirvana/latest), set the volume type to `nvme`.
For separately managed `nirvana_compute_volume` resources:
```hcl
resource "nirvana_compute_volume" "example_compute_volume" {
name = "my-data-volume"
type = "nvme"
size = 100
vm_id = nirvana_compute_vm.id
}
```
For `nirvana_compute_vm` with nested `boot_volume` and `data_volumes` fields:
```hcl
resource "nirvana_compute_vm" "vm" {
region = var.region
name = "my-vm"
os_image_name = data.nirvana_compute_vm_os_images.vm_os_images.items[0].name
ssh_key = {
public_key = var.ssh_public_key
}
cpu_config = {
vcpu = var.cpu
}
memory_config = {
size = var.memory
}
boot_volume = {
size = var.boot_disk_size
type = "nvme"
}
data_volumes = [
{
name = "my-data-volume"
size = var.data_disk_size
type = "nvme"
}
]
subnet_id = nirvana_networking_vpc.vpc.subnet.id
public_ip_enabled = true
tags = var.tags
}
```
---
title: Introduction to Nirvana Cloud
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/introduction/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/introduction/index.md
---
Nirvana Cloud is a Web3-native cloud provider designed to reduce cloud centralization and promote a decentralized infrastructure, especially in underserved regions. The platform is optimized for efficient data processing, tailored specifically for Web3 workloads. Utilizing selected CPUs optimized for rapid cryptographic calculations, Nirvana Cloud achieves higher transactions per second, ensuring rapid data processing and maximizing throughput for demanding applications.
Nirvana Cloud is engineered specifically for high-performance web3 applications. Developed by the Nirvana Labs team, its unique features include an ultra-lightweight hypervisor and an advanced software-defined networking layer. Unlike traditional cloud providers, Nirvana Cloud's innovative approach positions it at the forefront of both Web2 and Web3 sectors.
Nirvana Cloud stands at the forefront of this paradigm shift, championing infrastructure decentralization. Our model sets a new standard by replacing massive centralized data centers with a globally distributed network of Points of Presence (PoPs). This strategic alignment with top-tier data center providers worldwide ensures genuine infrastructure diversity.
## Data center Diversity
Our decentralized approach offers multiple advantages:
• **Resilience**: A decentralized model curtails the risk of widespread failures. Localized disruptions remain isolated, safeguarding system integrity.\
• **Performance**: With global PoPs, user requests are processed closer to their origin, slashing latency and delivering a stellar user experience.\
• **Redundancy**: Our infrastructure dynamically reroutes traffic based on data center metrics, ensuring seamless service continuity.
This strategy aligns with the fundamental concepts of decentralization, taking them a step further. Nirvana Cloud not only decentralizes the software and platform aspects but also extends this decentralization to the physical infrastructure, thereby strengthening user confidence.
## Web3 vs. Traditional Cloud Providers
Web3's revolutionary shift towards decentralization clashes with the centralized anchors of traditional Web2 cloud giants. These behemoths often eclipse the core values web3 stands for. A glaring example is the alarming reliance of Ethereum nodes on centralized cloud services, posing operational risks and potential biases. To ensure Web3 achieves its transformative potential, a shift to cloud solutions resonating with its decentralized spirit is paramount.
### Performance, Scalability, and Reliability Tailored for Web3
Nirvana Cloud is meticulously crafted to cater to Web3's unique demands:
• **Computational Power**: Our infrastructure boasts CPUs with unmatched clock speeds, ensuring top-tier performance for cryptographic operations.\
• **Memory Operations:** Our focus on low-latency RAM ensures seamless smart contract functionalities and interactions with the global state.\
• **Storage Efficiency**: With NVMe SSDs at the helm, our storage solutions are primed for the burgeoning datasets of blockchains.\
• **Networking**: Our P2P-centric networking stack ensures high-speed data transmissions, striking the ideal balance between latency and throughput.
At the core of Nirvana Cloud is a commitment to reliability. We ensure unwavering service availability with redundant systems, failover protocols, and best-in-class backup solutions, setting a new gold standard in the Web3 cloud domain.
---
title: What are the advantages of Nirvana Cloud?
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/introduction/advantages/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/introduction/advantages/index.md
---
Nirvana Cloud's architecture is designed to meet the needs of high-performance Web3 workloads and traditional Web2 environments. The hardware stack behind Nirvana Cloud is optimized for rapid data processing and maximum throughput, offering several considerable advantages over traditional cloud platforms:
## Low Latency, High Throughput
Nirvana Cloud's architecture is designed to minimize overheads, ensuring rapid data processing for demanding applications. Our optimized hardware stack, specifically tailored for Web3 workloads, includes handpicked CPU options that excel at solving complex cryptographic equations quickly. This investment reflects our commitment to delivering an infrastructure optimized for rapid data processing and high transaction throughput.
## Bandwidth Cost Optimization
A simplified software-defined networking stack allows Nirvana Cloud to streamline data routing, reducing redundant transfers and maximizing bandwidth utilization. Through key relationships and negotiations with carrier network providers, we offer a competitive unit cost, surpassing what traditional cloud providers typically offer, resulting in substantial cost savings for our users.
## Minimal Virtualization
Leveraging the power of minimal virtualization, Nirvana Cloud prioritizes direct hardware access. By minimizing the layers of virtualization, we ensure that applications experience reduced storage latency and can harness near-native performance from the underlying hardware. This design allows us to support an infrastructure where data processing is swift, storage responsiveness is immediate, and overall system performance is maximized.
## CPU & RAM Scalability
Nirvana Cloud's platform features a bare metal hypervisor design that prioritizes adaptability and scalability. Applications can adjust resources in real time, ensuring consistent performance. Users can create virtual machines with any combination of CPUs, RAM, and Storage, eliminating the issue of underutilized or overutilized resources commonly encountered with other cloud providers.
## Resilience & Reliability
Nirvana Cloud prioritizes high application uptime and performance. Our infrastructure incorporates time-tested open-source technologies, ensuring stability and optimal performance. We automatically back up every virtual machine storage volume to secure buckets, ensuring data integrity. With a global presence in over 20 regions and multiple Points of Presence (PoPs) worldwide, users can leverage multi-regional VPC peering to construct resilient, high-availability workloads. Our partnerships with premier data center providers ensure consistent power, efficient cooling, and swift access to essential components, strengthening our commitment to uninterrupted service.
## Web3-Focused Tooling
Nirvana Cloud provides developers with specialized toolsets to facilitate the transition and deployment of Web3 applications. Our core products, such as VPCs and VMs, are designed from the hardware to the networking layer with web3 workloads in mind. Our services extend to specialized storage solutions. Looking ahead, we plan to introduce sophisticated cryptographic services, critical for the burgeoning DeFi sector.
## Security & Privacy
Nirvana Cloud places a paramount focus on security and privacy. Our infrastructure is safeguarded with comprehensive encryption, a zero-trust model, continuous security assessments, and isolation techniques for user workloads. Committed to global compliance standards, Nirvana is SOC2 certified.
Furthermore, Nirvana Cloud blends software and hardware security measures designed specifically for web3 developers to ensure a robust cryptographic environment.
---
title: What are common use cases for Nirvana Cloud?
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/introduction/use-cases/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/introduction/use-cases/index.md
---
Nirvana Cloud's infrastructure is specifically constructed to excel with decentralized workloads, offering optimized performance for scenarios that require high requests per second (RPS), minimal latency, and exceptional reliability. It is designed with the foresight to handle the rigorous demands of Web3 applications, such as cryptocurrency transactions, smart contracts, and decentralized finance (DeFi) services, which necessitate swift and secure data processing capabilities.
At the same time, Nirvana Cloud is equally adept at supporting the traditional needs of Web2 applications. This ensures that organizations that rely on standard web services for e-commerce, content delivery networks, and enterprise systems can leverage Nirvana Cloud's robustness and reliability. With its dual-use capability, Nirvana Cloud is an ideal platform for businesses looking to operate within the Web2 ecosystem while preparing for the transition to or incorporation of Web3 technologies, allowing for a broad range of use cases from legacy systems to cutting-edge decentralized applications.
### Web3-specific use cases
**Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)**: Nirvana Cloud ensures swift settlement of trades and order book updates on DEXs, enhancing user experience with its high RPS support and low latency.
**Blockchain-based Gaming Platforms**: Real-time asset transfers and game player-vs-player actions require high RPS and low latency. Nirvana Cloud enables smooth gameplay, accommodating a large number of simultaneous players.
**Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Platforms**: Financial transactions on lending or derivatives platforms need to adapt quickly to market conditions. Nirvana Cloud can support the rapid-response requirements of DeFi applications.
**Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs):** Speed and reliability are crucial for DAOs conducting voting or consensus mechanisms. DAOs on Nirvana Cloud can ensure prompt member action processing, reflecting real-time governance changes.
**Supply Chain dApps**: Decentralized supply chain solutions rely on high RPS and low latency for real-time goods movement updates, ensuring accurate tracking.
**Decentralized Content Delivery Platforms**: Nirvana Cloud's low latency guarantees uninterrupted content delivery, even during demand surges. This is crucial for web3 streaming or content-sharing platforms.
**NFT Marketplaces:** Nirvana Cloud guarantees seamless NFT listings, bids, and transfers.
**Oracles**: Oracles that provide external data to blockchains require high RPS and low latency for timely data delivery to dependent smart contracts. Nirvana Cloud meets these essential requirements.Cross-Chain Bridges: For dApps operating across multiple blockchains, swift and reliable inter-chain communication is pivotal. Nirvana Cloud facilitates smooth transfers of tokens or data across different blockchains.
**Custodial Platforms**: Secure and reliable operations are crucial for custodial platforms that hold cryptocurrencies, NFTs, or other digital assets. Nirvana Cloud provides an environment where transactions, withdrawals, and deposits are processed quickly and securely.
**Web Hosting**: Nirvana Cloud's scalable infrastructure is suitable for web hosting, supporting everything from small personal blogs to large e-commerce sites. Its decentralized nature ensures high uptime and resistance to DDoS attacks, while high RPS and low latency contribute to fast-loading web pages, critical for SEO and user satisfaction.
### Web2-specific use cases
**Databases**: Nirvana Cloud guarantees quick data access speeds for distributed databases requiring high transaction throughput, ensuring consistent performance even under heavy load. This facilitates real-time analytics and transaction processing for Web3 applications.
**Mail Servers**: Nirvana Cloud enables high availability of global Points of Presence (PoPs), making secure and efficient handling of email traffic possible. The network's decentralized nature can significantly reduce the risk of downtime and mail service disruptions.
**Applications (Frontend/Backend)**: Nirvana Cloud supports diverse application workloads, offering developers the ability to scale resources for both frontend interfaces and backend processing as needed. It delivers an agile environment to deploy microservices, APIs, and full-stack applications with consistent performance and reliability.
**Kubernetes/Containerization Environments**: Nirvana Cloud is well-suited for Kubernetes and other container orchestration systems, providing a resilient infrastructure for container deployment and management. It enhances the deployment of microservices and dynamic scaling of workloads with high efficiency and minimal latency.
**Backup Servers**: With Nirvana Cloud, backup systems become more reliable and secure, offering decentralized storage solutions to protect against data loss and outages. Its high RPS capabilities ensure quick backup and restore operations, an essential feature for disaster recovery strategies.
**File Servers**: Nirvana Cloud's file servers benefit from its decentralized structure, allowing for secure and speedy file access and sharing across the globe. High RPS allows for multiple concurrent file transfers without bottlenecks, which is vital for collaboration in Web3 spaces.
**Game Servers**: Resource and traffic-intensive games can rely on Nirvana Cloud to optimize the gaming experience by hosting game servers that require high RPS to manage the state of play for numerous concurrent users. Low latency is vital for real-time multiplayer games, ensuring fair and responsive gameplay.
By catering to these decentralized workloads with high throughput, reduced latency, and unparalleled reliability, Nirvana Cloud establishes itself as an indispensable infrastructure ally for the evolving web3 ecosystem.
---
title: Networking
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/index.md
---
Networking plays an integral role in all use cases, as it enables seamless connectivity and communication of the various components within your deployed architecture. Nirvana Cloud provides a variety of networking tools and services that can be leveraged for efficient, reliable, and secure communication.
## Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
One essential feature of Nirvana Cloud is its Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), which allows you to provision a logically isolated section of the cloud. The VPC provides the environment within which you can deploy your applications securely and is isolated from other Virtual Private Clouds.
## Site to Site Mesh
A site-to-site mesh involves interconnecting subnets in different locations via our mesh network enabling a secure communication channel between them. It is analogous to extending a private network across the internet and allowing resources to communicate as if these locations are on the same local network.
Overall, Nirvana Cloud's robust networking features are designed to provide scalable and secure environments for businesses to deploy applications and databases seamlessly. To ensure optimal performance and security, understanding the functioning of Nirvana Cloud's networking is crucial.
---
title: Overview
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/connect/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/connect/index.md
---
Nirvana Connect is a dedicated, low-latency, private interconnect fabric that links Nirvana Cloud directly to external cloud providers such as AWS, GCP, and Azure. Unlike the public internet, Nirvana Connect establishes dedicated fiber circuits through reserved private network paths, enabling secure, high-performance data transfer with predictable latency and enhanced reliability.
## How It Works
Nirvana Connect leverages a Tier 1 global infrastructure provider to provision private virtual circuits that directly connect Nirvana Cloud to major cloud providers. These circuits use existing fiber infrastructure already laid between data centers and cloud providers.
Instead of installing new physical cables, Nirvana reserves bandwidth on these private links to create dedicated, secure, high-speed connections between environments. Because data travels through a private path rather than the public internet, traffic avoids standard egress fees, reduces congestion, and gains stable, predictable throughput.
Nirvana covers the infrastructure costs, so you don't have to.
## Key Features
- **Private fiber connections** between Nirvana Cloud and major cloud providers (AWS, GCP, Azure)
- **Sub-millisecond latency** unaffected by public traffic
- **Pre-provisioned infrastructure** requiring no new physical installation
- **Quick activation** through the dashboard, API, Terraform and all SDKs
- **Multiple bandwidth tiers** from 50 Mbps to 2 Gbps
## Benefits
### Eliminate Egress Fees
By bypassing the public internet, Nirvana Connect removes standard egress charges entirely. This can reduce data transfer costs by up to 90% compared to traditional public internet routing between cloud environments.
### Lower Latency
Dedicated private circuits deliver sub-millisecond latency unaffected by public traffic. Fewer network hops and direct connectivity ensure consistent uptime for latency-sensitive operations.
### Enhanced Security
Data traverses private, isolated network paths rather than the public internet. This isolation provides enhanced security and privacy while preserving your existing IP and security rules. It also makes it easier to maintain compliance across multi-cloud environments.
### Stable, Predictable Throughput
Private circuits maintain reliable performance independent of public network congestion. This stability is critical for high-frequency trading, real-time systems, and other operations that require consistent network behavior.
### Multi-Cloud Flexibility
Seamlessly integrate multiple cloud providers without being tied to a single ecosystem. Offload Web3-intensive workloads to Nirvana Cloud while maintaining existing cloud setups on AWS, Azure, or GCP.
## Use Cases
### Blockchain Node Operations
Run blockchain nodes on Nirvana Cloud while hosting indexers, frontends, or supporting services on other cloud providers. Nirvana Connect ensures high-bandwidth, stable connectivity between these components while keeping node infrastructure isolated from the public internet.
### High-Frequency Trading
HFT operations in Web3 depend on ultra-fast, deterministic latency between trading systems and blockchain nodes. Nirvana Connect provides dedicated, low-latency circuits, redundant paths, and congestion-free routing to optimize execution speed and reliability.
### Kubernetes Cluster Mesh
Teams running Kubernetes across multiple clouds can use Nirvana Connect to enable CNI-level networking (e.g., with Cilium), allowing pods and services to communicate seamlessly across providers. Direct, secure connectivity improves service mesh performance, reduces latency, and lowers inter-cluster traffic costs.
### Hybrid Multi-Cloud Architectures
Host Elasticsearch on Nirvana while ingesting data from third-party providers. Run RPC nodes on Nirvana while maintaining AWS application services. Any scenario requiring large-volume data transfer between clouds at scale benefits from private connectivity.
## Supported Regions
Nirvana Connect currently operates private network hubs in:
- Seattle (us-sea-1)
- Silicon Valley (us-sva-1)
- Chicago (us-chi-1)
- Washington, D.C. (us-wdc-1)
- Frankfurt (eu-frk-1)
- Singapore (ap-sin-1)
- Seoul (ap-seo-1)
- Tokyo (ap-tyo-1)
## Supported Cloud Providers
Currently, Nirvana Connect supports direct interconnect to **AWS**. Additional providers are coming soon.
## Pricing
Nirvana Connect is currently in a trial period, free for all Nirvana Cloud users. Pricing will be introduced after the trial, with options for partners and dedicated interconnects.
## Next Steps
Ready to set up your private connection? Follow the [Set up AWS Direct Connect](/cloud/networking/connect/how-to/set-up-aws-direct-connect/) guide to create your first connection between Nirvana Cloud and AWS.
For more details, see the [FAQ](/cloud/networking/connect/faq/).
## FAQ
What bandwidth options does Nirvana Connect support?
Nirvana Connect currently supports the following bandwidth tiers:
- 50 Mbps
- 200 Mbps
- 500 Mbps
- 1 Gbps
- 2 Gbps
How much can I save?
By eliminating per-GB egress billing, Nirvana Connect can reduce data transfer costs by up to 90% compared to traditional public internet routing between cloud environments.
There are no Nirvana egress fees, and AWS egress rates over Direct Connect are typically around $0.02 per GB, compared to roughly $0.09 per GB over the public internet.
Where is the private fiber from?
Nirvana Connect runs on private fiber provided through Nirvana's long-term infrastructure partner, linking Nirvana Cloud directly to major cloud providers.
---
title: FAQ
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/connect/faq/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/connect/faq/index.md
---
## What is Nirvana Connect?
Nirvana Connect is a private interconnect service (aka a private internet connection) that establishes dedicated fiber circuits between Nirvana Labs, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and other major cloud providers.
Unlike the public internet, Nirvana Connect links these environments through reserved private network paths, **enabling** secure, high-performance data transfer with predictable latency and enhanced reliability. This integration allows applications and data to move freely between multiple clouds, letting teams treat them as a single, unified network.
## How does Nirvana Connect work?
Nirvana Connect works by leveraging a Tier 1 global infrastructure provider to provision private virtual circuits that directly connect Nirvana Cloud to major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
These circuits use existing fiber infrastructure already laid between data centers and the cloud providers. Instead of installing new physical cables, Nirvana reserves bandwidth on these private links to create dedicated, secure, high-speed connections between environments — giving users faster, more reliable network performance and meaningful cost savings.
In short, Nirvana covers the infrastructure costs, so you don't have to.
Because data travels through a private path rather than the public internet, customers avoid standard egress fees, reduce congestion, and gain stable, predictable throughput. Customers can self-provision these circuits through the Nirvana Cloud dashboard or API, enabling flexible and scalable connectivity.
## Who is Nirvana Connect for?
Nirvana Connect is available to all Nirvana Cloud users.
It's designed for teams running workloads such as:
- Node runners and RPC infrastructure
- Indexers and blockchain analytics
- Cross-chain infrastructure and messaging
- Real-time backend and transaction systems
- High-frequency and latency-sensitive applications
## What are the benefits of using Nirvana Connect?
**Lower latency and high availability**
- Dedicated private circuits provide predictable, low-latency performance compared to public internet.
- Fewer network hops and direct connectivity ensure consistent uptime for latency-sensitive operations.
**Enhanced security and compliance**
- Data traverses private, isolated network paths for enhanced security and privacy.
- Easier to maintain compliance across multi-cloud environments.
**Flexible workload management**
- Offload Web3-intensive workloads to Nirvana Cloud while maintaining existing cloud setups on AWS, Azure, or GCP.
- Efficiently allocate resources across providers based on performance or regulatory needs.
**Cost optimization**
- By bypassing the public internet, Nirvana Connect avoids standard egress charges.
- Greater cost savings at higher transfer volumes.
**Freedom from vendor lock-in**
- Seamlessly integrate multiple cloud providers without being tied to a single ecosystem.
## What are common use cases for Nirvana Connect?
**High-Frequency Trading**
HFT operations in Web3 depend on ultra-fast, deterministic latency between trading systems and blockchain nodes.
Nirvana Connect provides dedicated, low-latency circuits, redundant paths, and congestion-free routing to optimize execution speed and reliability.
**Blockchain Node Operations**
Many organizations run blockchain nodes on Nirvana Cloud while hosting indexers, frontends, or supporting services on other cloud providers.
Nirvana Connect ensures high-bandwidth, stable connectivity between these components while keeping node infrastructure isolated from the public internet.
**Kubernetes Cluster Mesh**
Teams running Kubernetes across multiple clouds can use Nirvana Connect to enable CNI-level networking (e.g., with Cilium), allowing pods and services to communicate seamlessly across providers.
Direct, secure connectivity improves service mesh performance, reduces latency, and lowers inter-cluster traffic costs.
## How much can I save?
By eliminating per-GB egress billing, Nirvana Connect can reduce data transfer costs by up to 90% compared to traditional public internet routing between cloud environments.
There are no Nirvana egress fees, and AWS egress rates over Direct Connect are typically around $0.02 per GB, compared to roughly $0.09 per GB over the public internet.
## Where does Nirvana Connect currently operate network hubs?
Nirvana Connect currently operates private network hubs in:
- Seattle (us-sea-1)
- Silicon Valley (us-sva-1)
- Chicago (us-chi-1)
- Washington, D.C. (us-wdc-1)
- Frankfurt (eu-frk-1)
- Singapore (ap-sin-1)
- Seoul (ap-seo-1)
- Tokyo (ap-tyo-1)
These hubs support enterprise and latency-sensitive workloads, providing direct, private connectivity between Nirvana Cloud and major cloud providers.
## How many cloud providers does Nirvana Connect support?
Currently, Nirvana Connect supports direct interconnect to AWS. Support for GCP can be enabled on demand in under 10 minutes.
Nirvana Connect can also support additional providers, including Microsoft Azure and Alibaba Cloud, as the network fabric is designed to scale flexibly to multiple providers.
## Where is the private fiber from?
Nirvana Connect runs on private fiber provided through Nirvana's long-term infrastructure partner, linking Nirvana Cloud directly to major cloud providers.
## What's the difference between Nirvana Connect and Nirvana Network?
Nirvana Connect supports self-connections, linking your own environments between Nirvana Cloud and other cloud providers.
Nirvana Network (coming soon) will enable cross-company private connections, allowing different Web3 providers on Nirvana Cloud to exchange data over the same private fiber backbone.
## What bandwidth options does Nirvana Connect support?
Nirvana Connect currently supports the following bandwidth tiers:
- 50 Mbps
- 200 Mbps
- 500 Mbps
- 1 Gbps
- 2 Gbps
## Is there a cost to use Nirvana Connect?
Nirvana Connect is currently in a trial period, free for all Nirvana Cloud users.
Pricing will be introduced after the trial, with options for partners and dedicated interconnects.
## How can I get started?
If you're already using Nirvana Cloud, you can activate Nirvana Connect directly from your dashboard or API.
New partners can [reach out to the team](https://nirvanalabs.io/contact) for onboarding support.
---
title: Set up AWS Direct Connect
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/connect/how-to/set-up-aws-direct-connect/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/connect/how-to/set-up-aws-direct-connect/index.md
---
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to set up Nirvana Connect to create a secure, private connection between your Nirvana VPC and your AWS (or any other cloud provider) environment.
Whether you’re logging in for the first time or configuring a production-grade private link, this guide will walk you through the entire process, from signing in, creating your first VPC, and provisioning a connection, to completing the setup on AWS.
## Step 0: Log in or Sign Up
1. Visit [dashboard.nirvanalabs.io](https://dashboard.nirvanalabs.io)
2. Log in with your credentials or click **Sign up** to create a new account
3. Once logged in, click **Cloud Dashboard** in the sidebar to access the main control panel
You will now see the **Compute**, **Storage**, and **Networking** menus in the navigation panel.
## Step 1: Create (or Verify) Your VPC
1. Navigate to **Networking → VPCs**
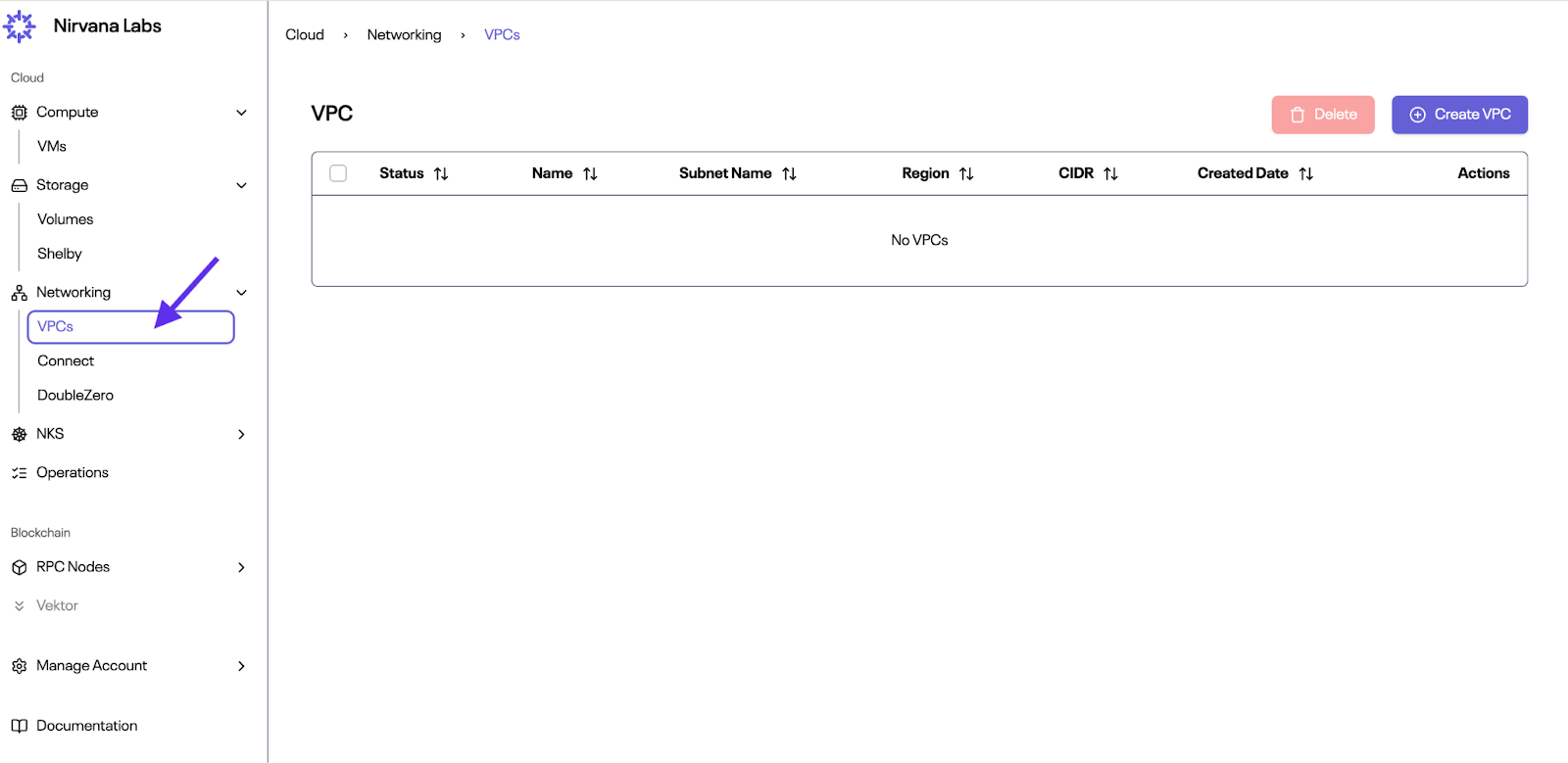
2. If this is your first time, the table will be empty. Click **Create VPC**
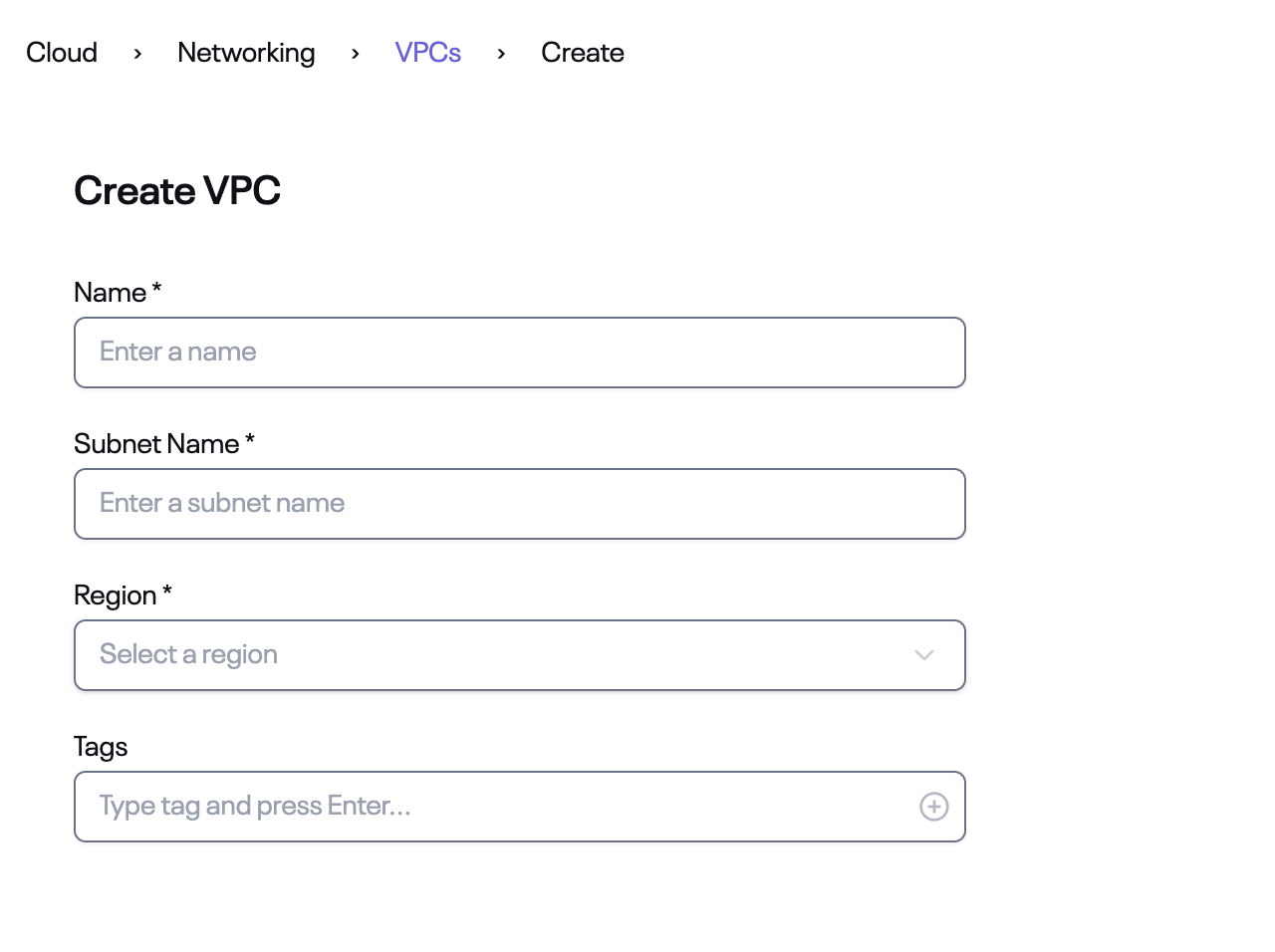
3. Fill in:
- Name
- Subnet Name
- Region
- (Optional) Tags
4. Click **Create**. Once created, the VPC will appear with **Status: Ready**
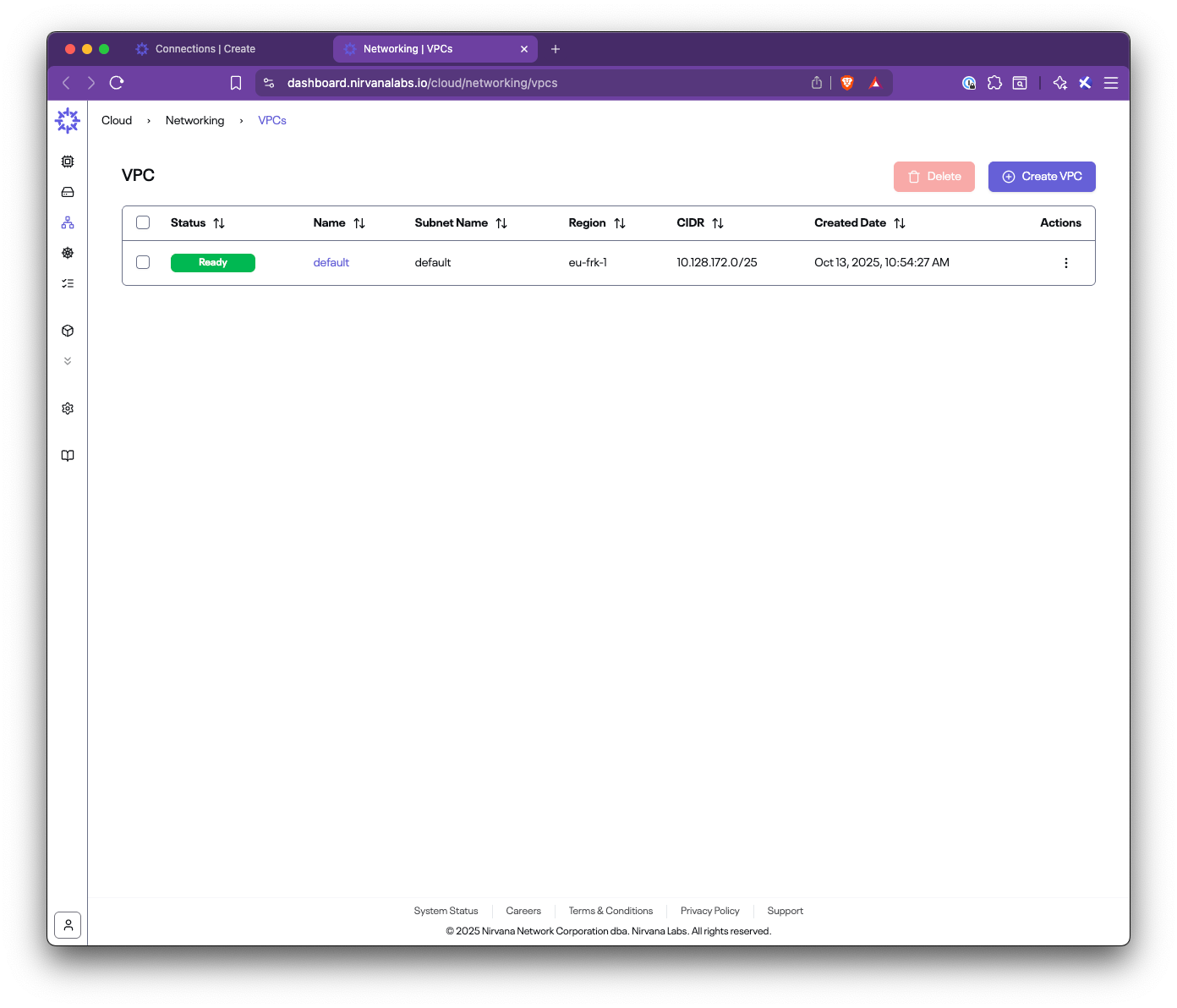
:::note
You need an existing VPC before creating a connection. Its CIDR will be advertised to AWS during the setup.
:::
## Step 2: Create a Connection
1. Navigate to **Networking → Connect → Connections**
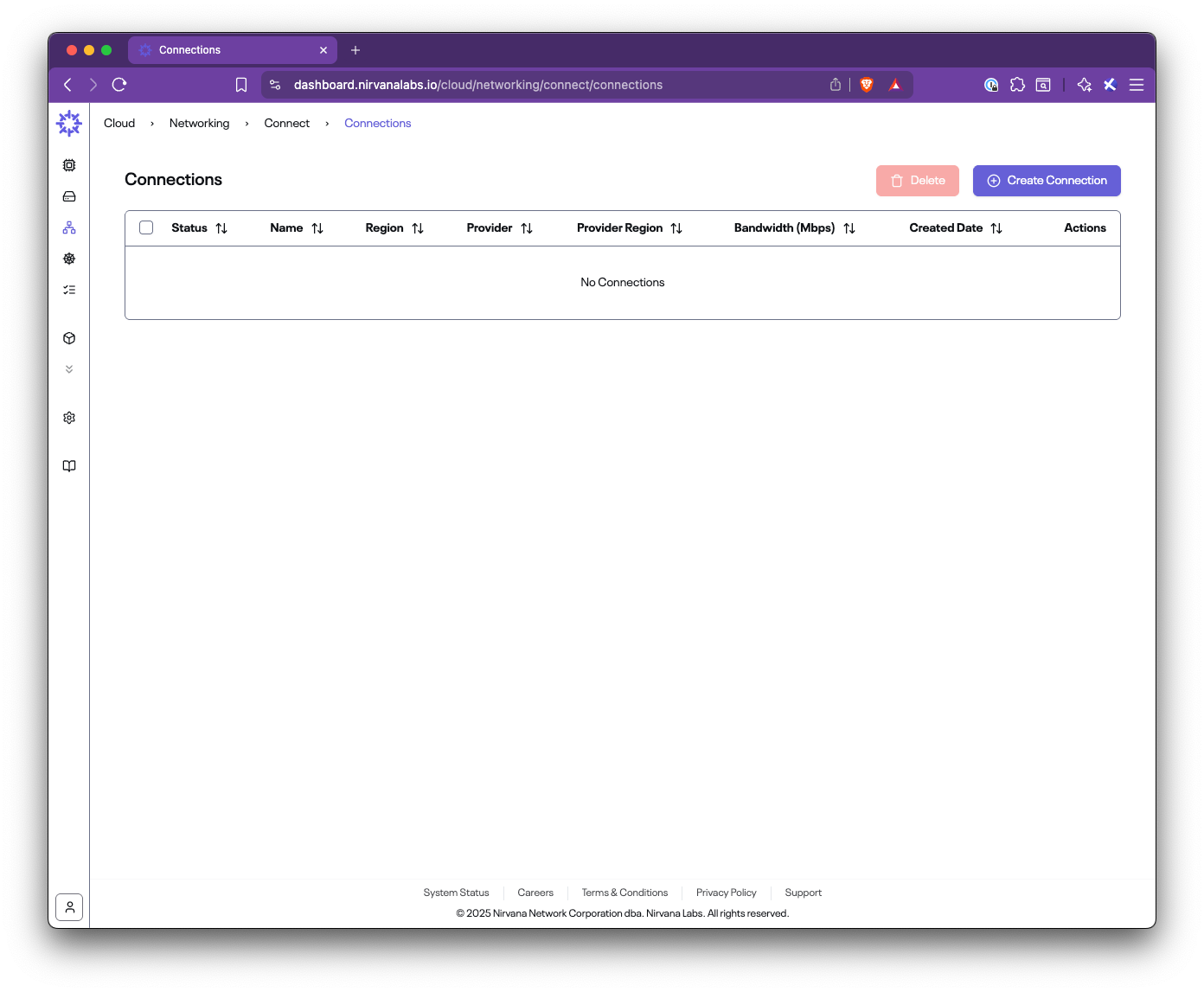
2. If this is your first time, the table will be empty. Click **Create Connection**
3. Fill out the form:
- **Name**: A descriptive connection name (e.g., `aws-connection`)
- **Region**: The Nirvana region where your VPC is located (e.g., `eu-frk-1`)
- **Bandwidth**: Choose the capacity (e.g., 50, 100, 500 Mbps)
- **CIDRs**: Select your Nirvana VPC CIDR
- **Provider Name**: AWS
- **Provider CIDRs**: Enter the AWS VPC CIDR or prefixes behind your TGW/VGW
- **AWS Account ID**: Your 12-digit AWS account ID
- **AWS Region**: The AWS region to connect to (e.g., `eu-central-1`)
- **Tags**: Optional metadata
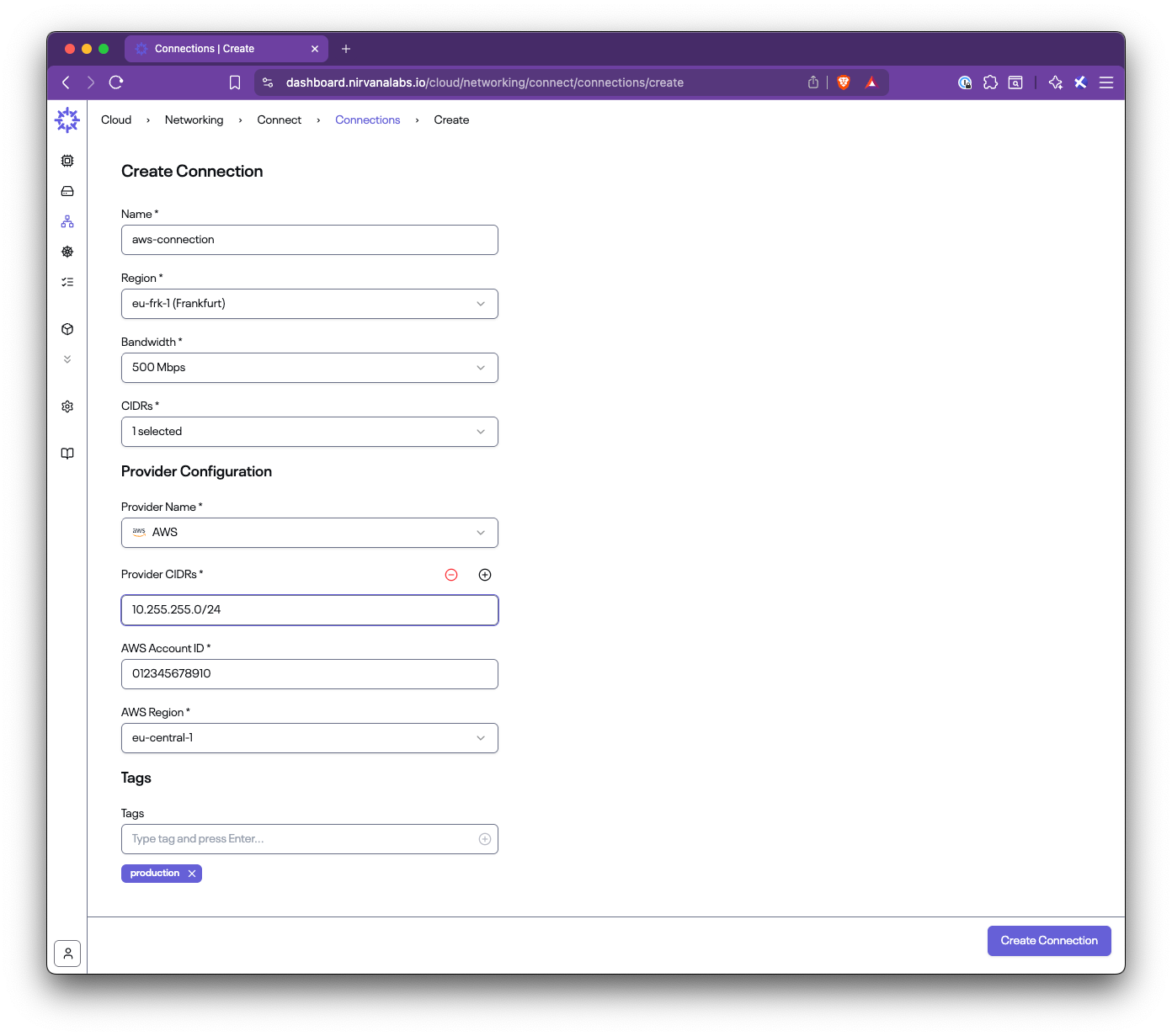
4. Click **Create Connection**
:::tip
**Provider CIDRs** represent the AWS-side networks you want Nirvana to route to. Nirvana will program routes on its end using this field. Nirvana VPC CIDRs and Provider CIDRs must not overlap.
:::
## Step 3: Check Connection Status and Parameters
1. After creating the connection, you will see it listed with **Status: Creating**
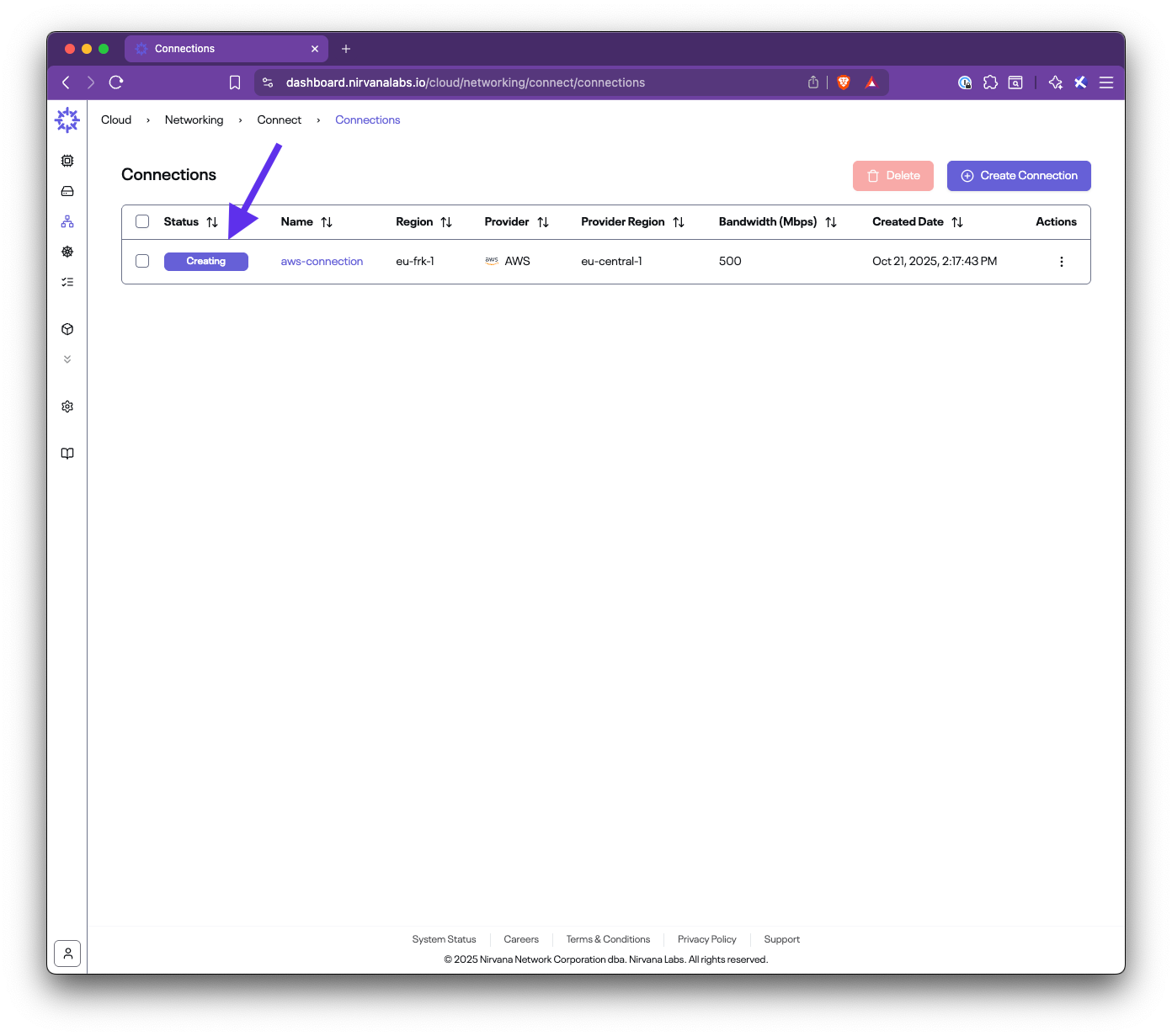
2. Once provisioning is complete, the status will change to **Ready**
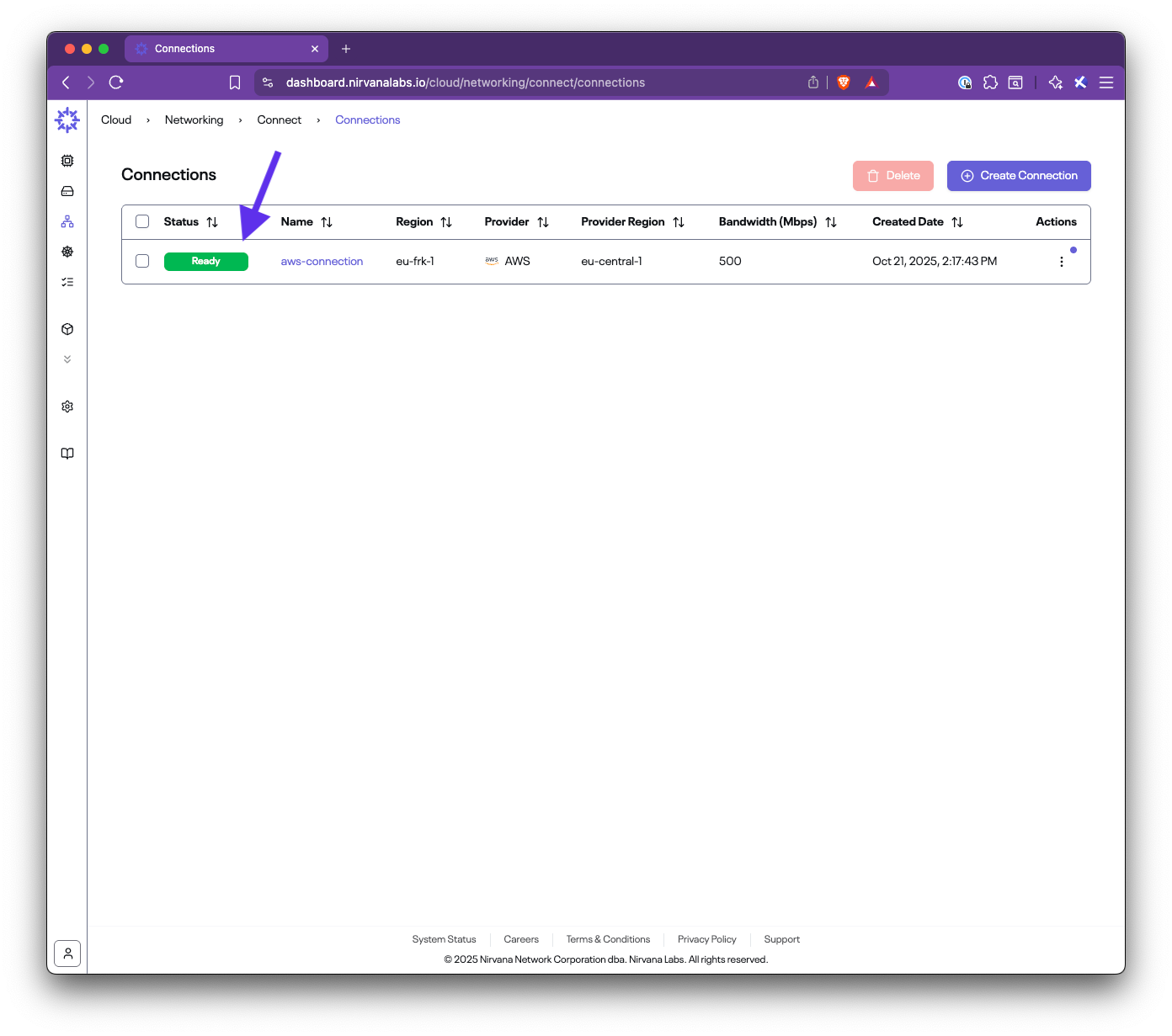
3. View connection details:
- Router IPs (Nirvana and AWS sides)
- ASNs for BGP configuration
- CIDRs
- Bandwidth (50 Mbps / 200 Mbps / 500 Mbps / 1 Gbps / 2 Gbps)
- Provider details
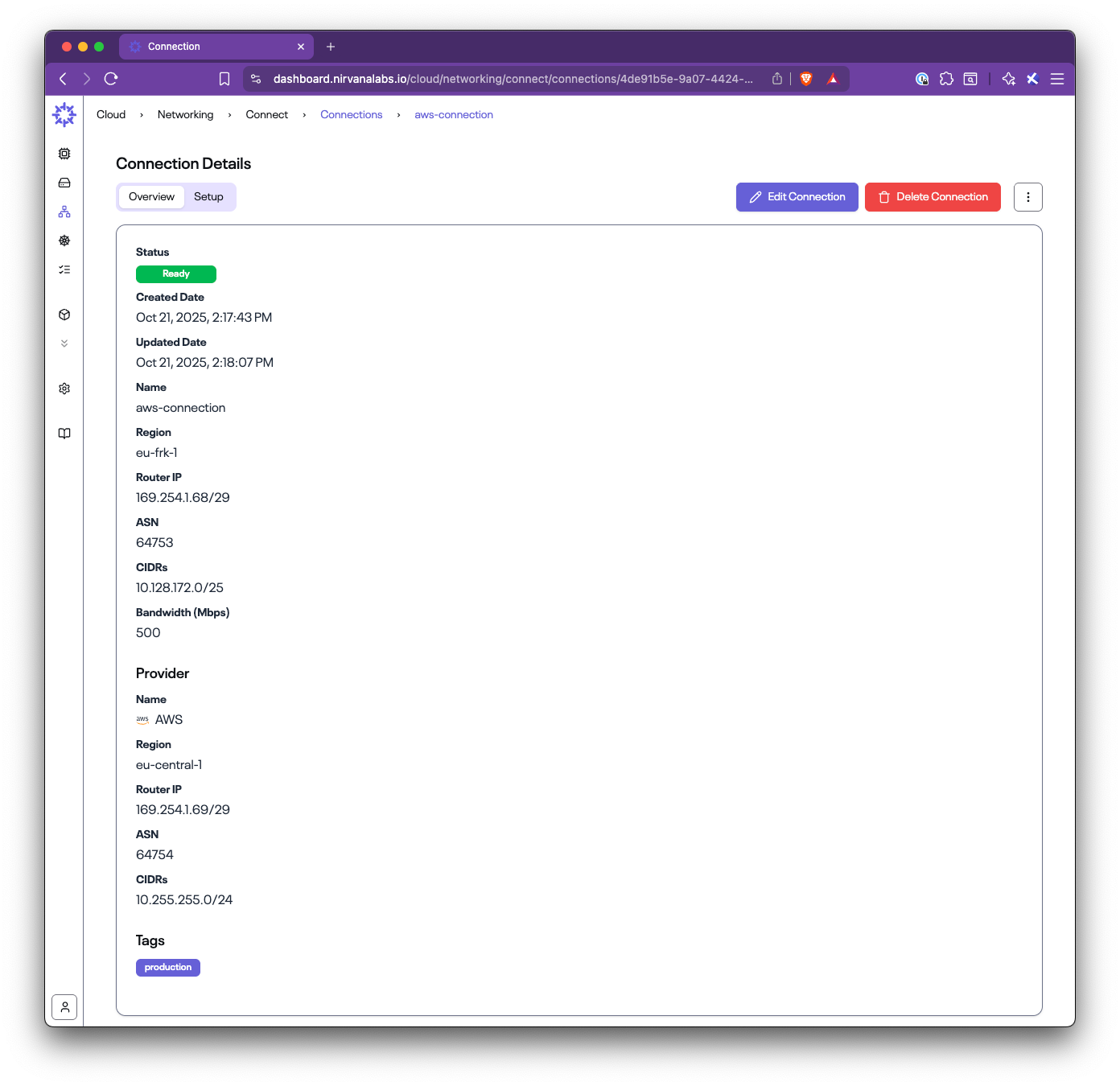
You will use these values when configuring AWS.
## Step 4: Run the Setup on AWS
From the connection list, open the menu under **Actions** and select **Setup Connection** (or open the Setup tab in the details view).
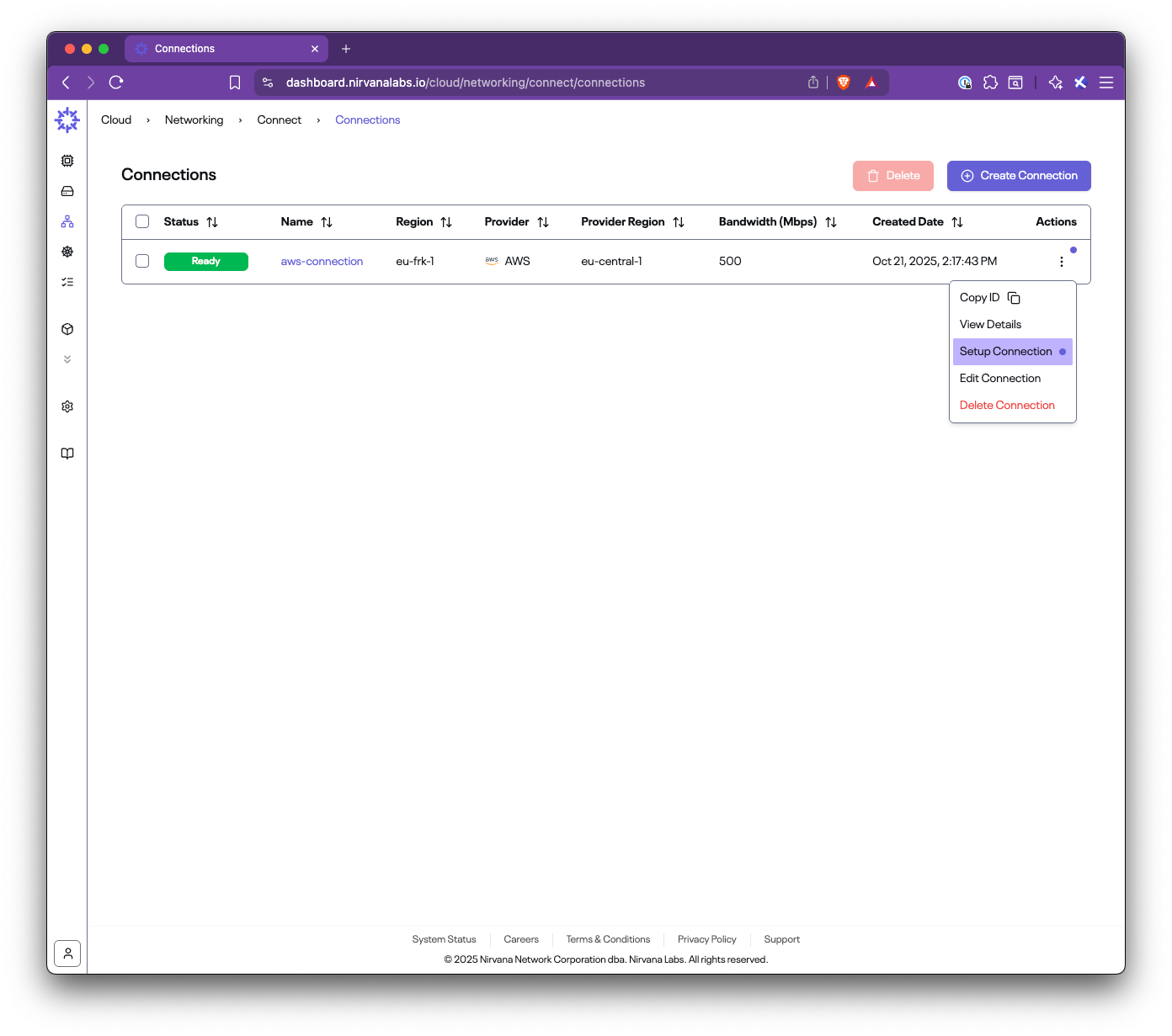
Follow the guided steps:
### Step 4.1: Accept the connection in AWS Direct Connect
1. Open the AWS Direct Connect console
2. Go to **Connections**
3. Find the pending connection with the name shown in the Setup panel
4. Accept and confirm
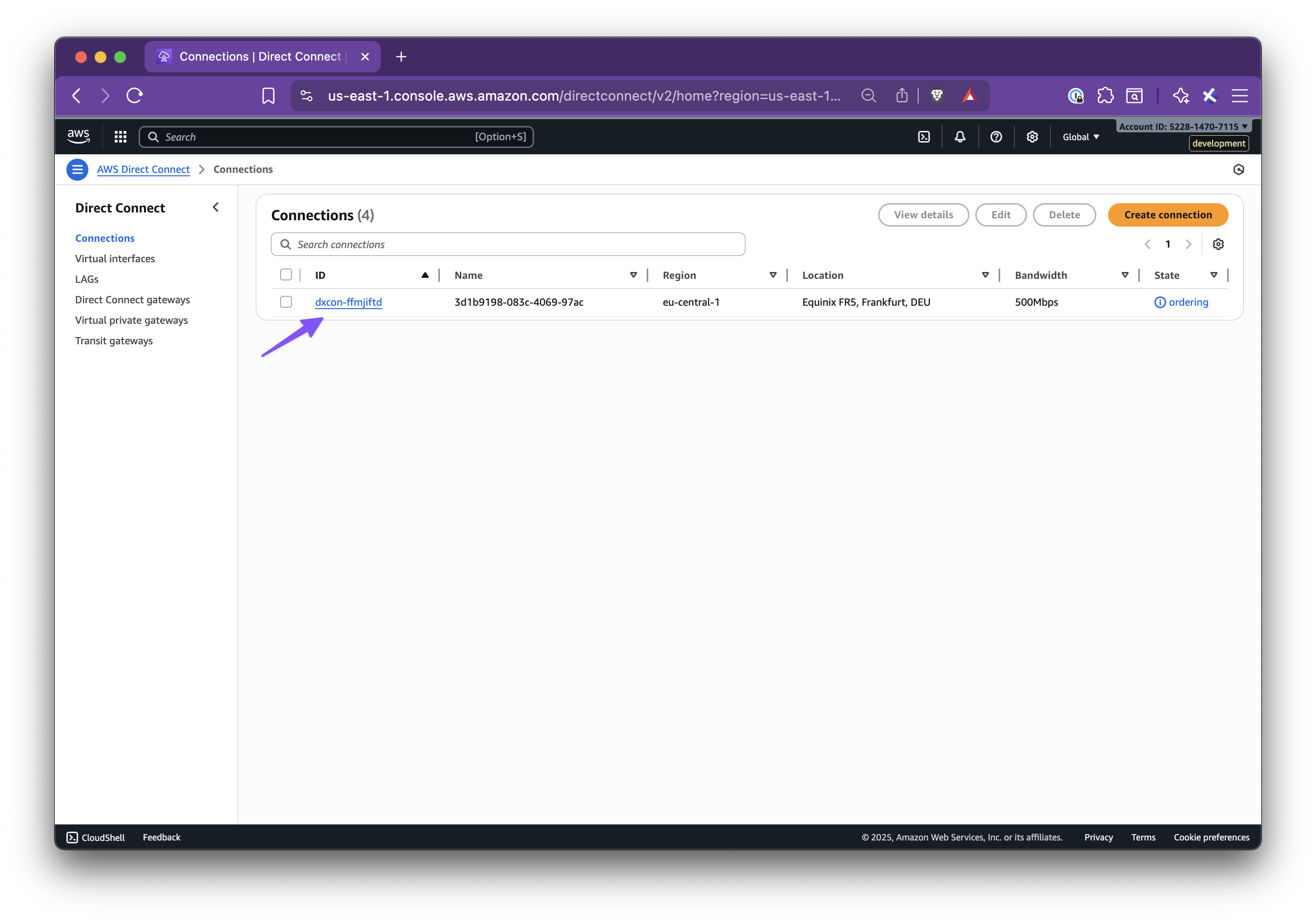
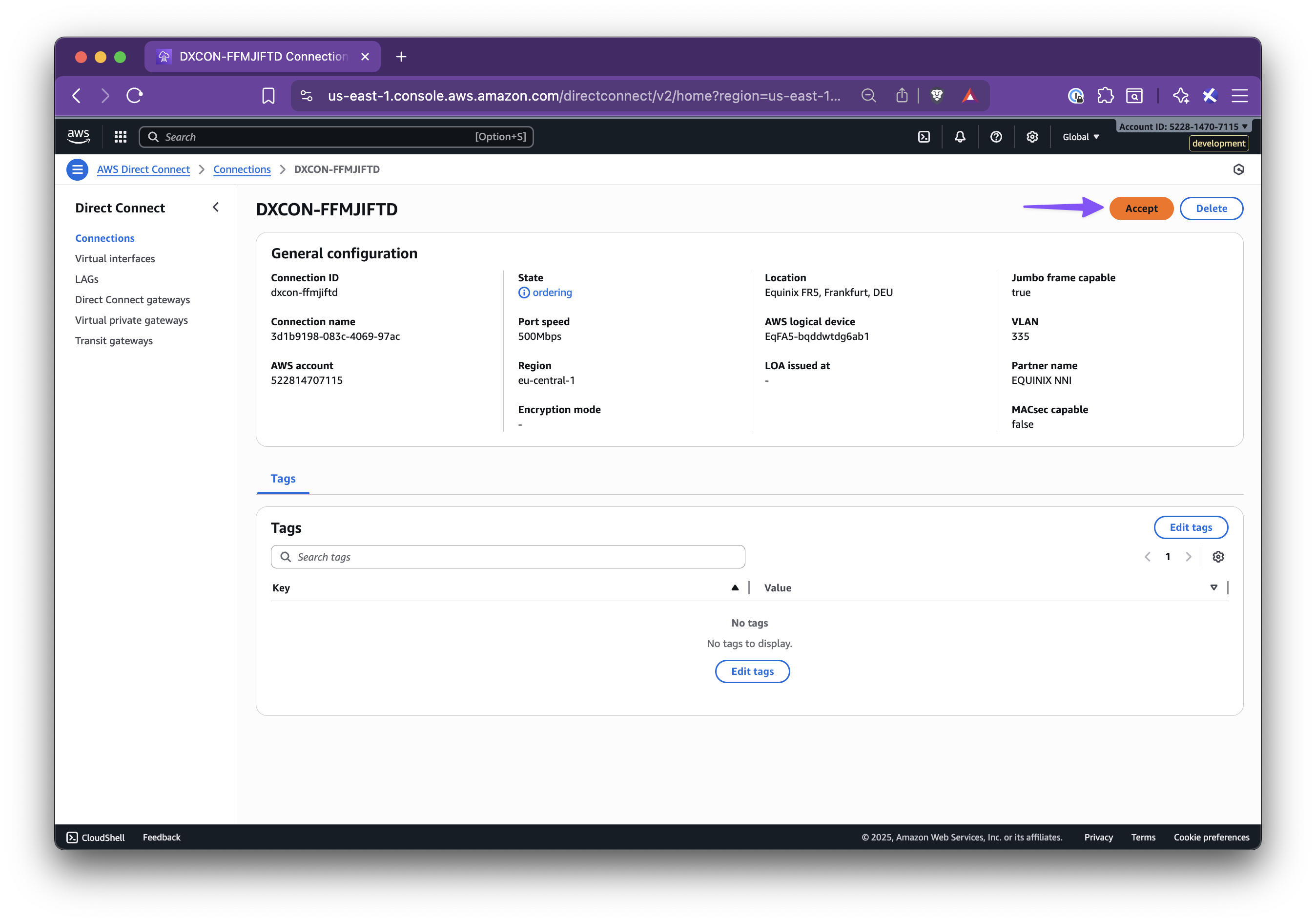
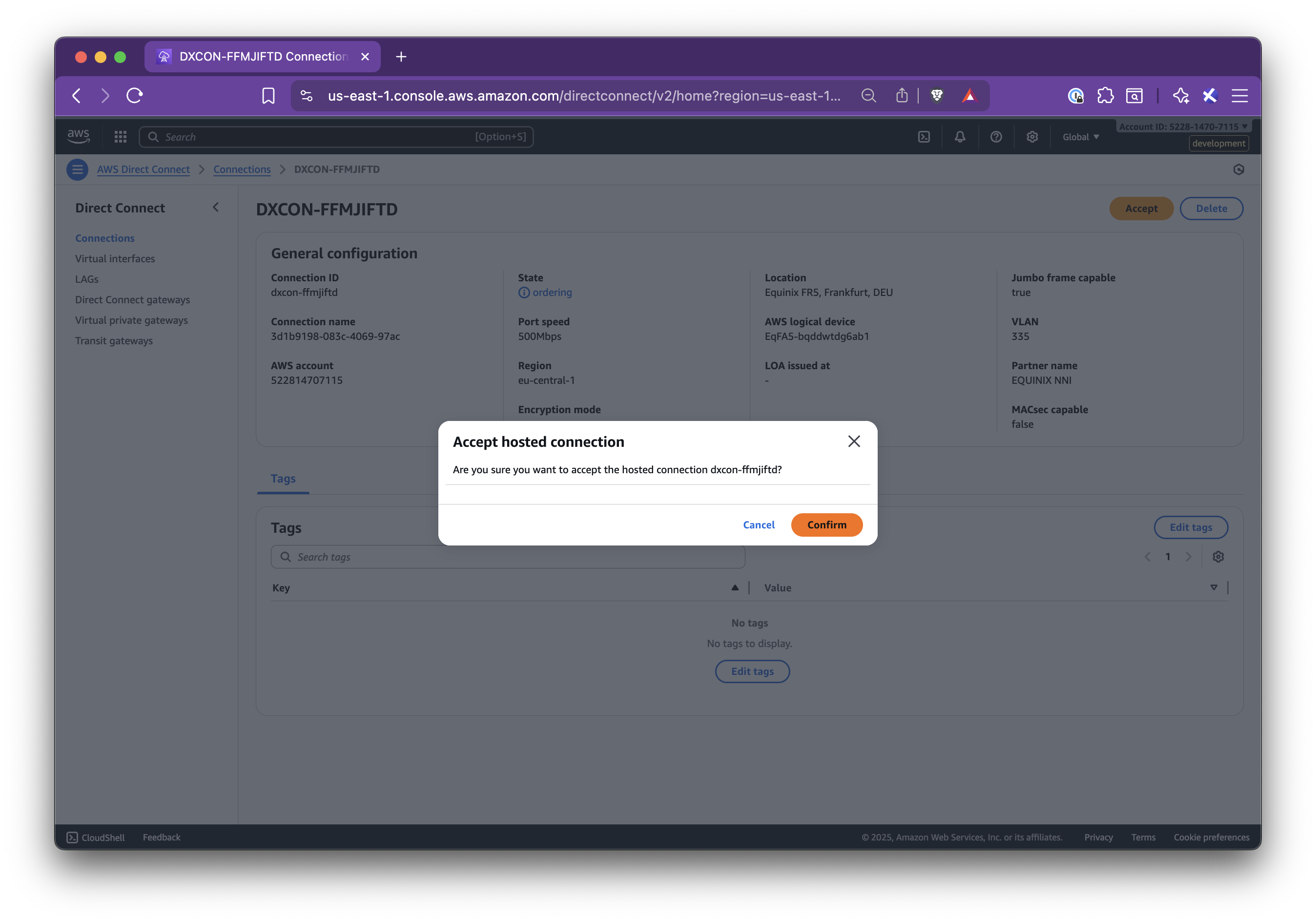
### Step 4.2: Create a Virtual Private Gateway (VGW)
1. Go to **AWS VPC → Virtual private gateways**
2. Create a new VGW with:
- **Name tag**: suggested name from the panel
- **ASN**: the AWS-side ASN shown in the panel
3. Click **Create virtual private gateway**
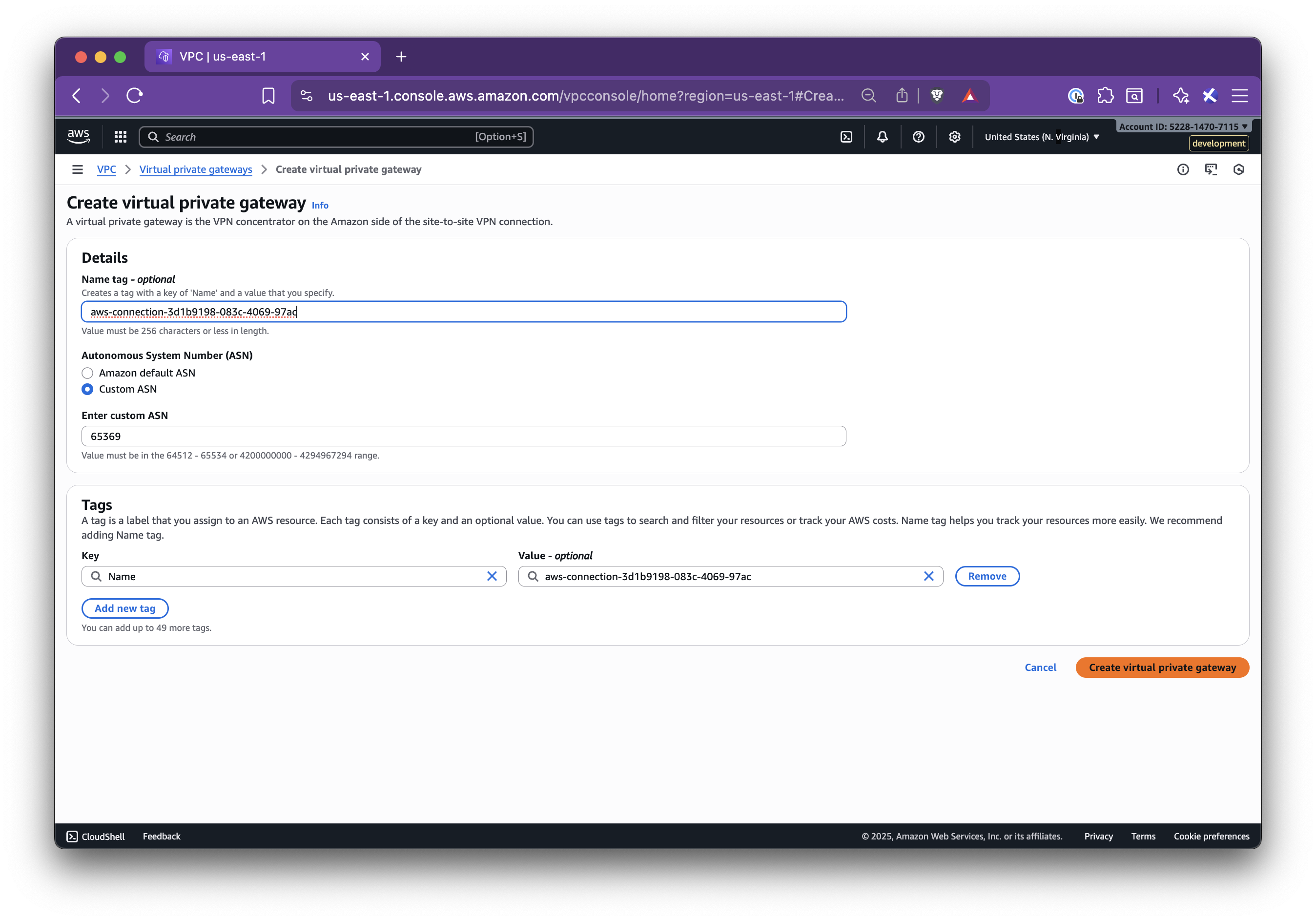
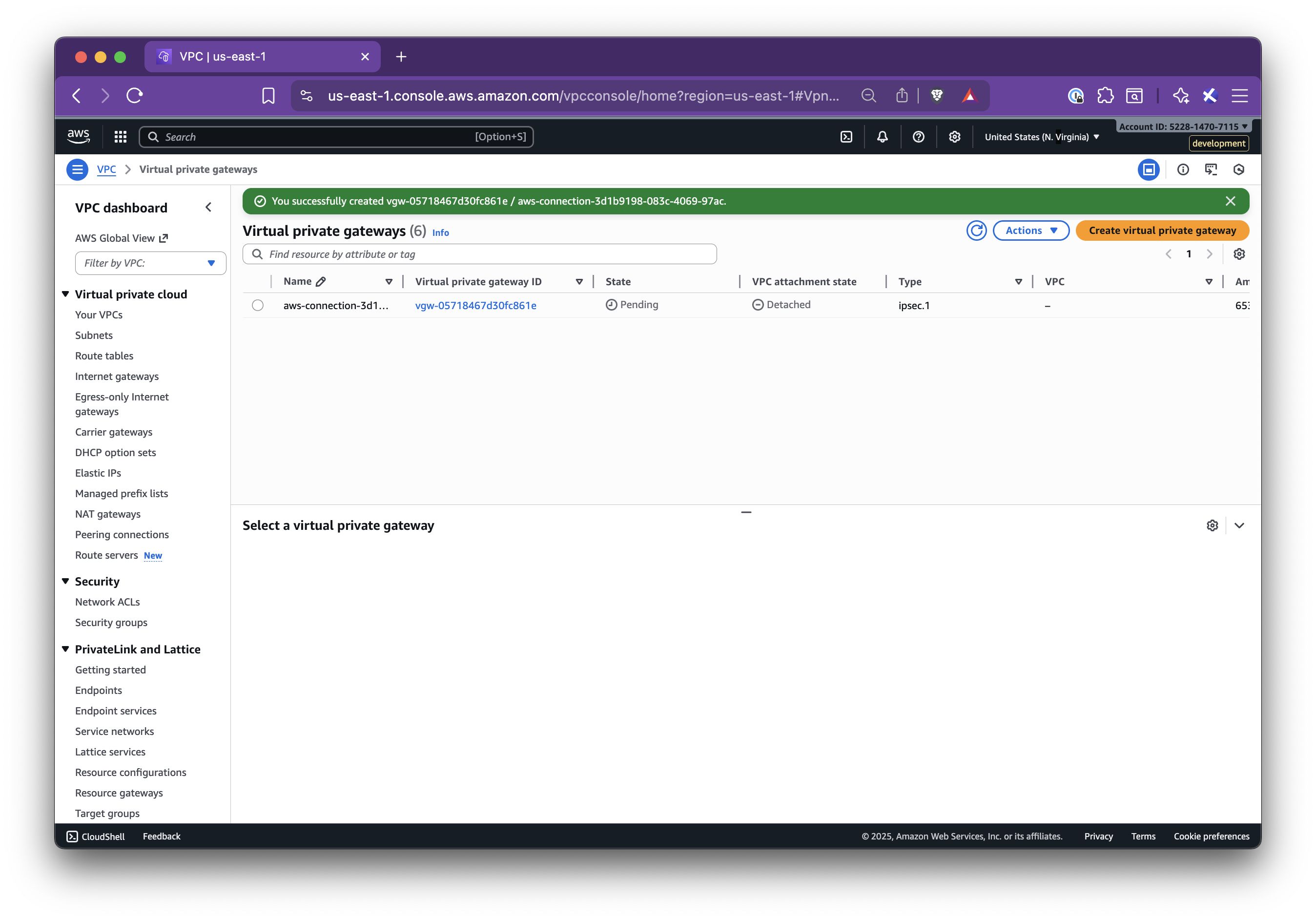
### Step 4.3: Attach the VGW to your VPC
1. In **Virtual private gateways**, select the new VGW
2. Click **Actions → Attach to VPC**
3. Select your target VPC and attach
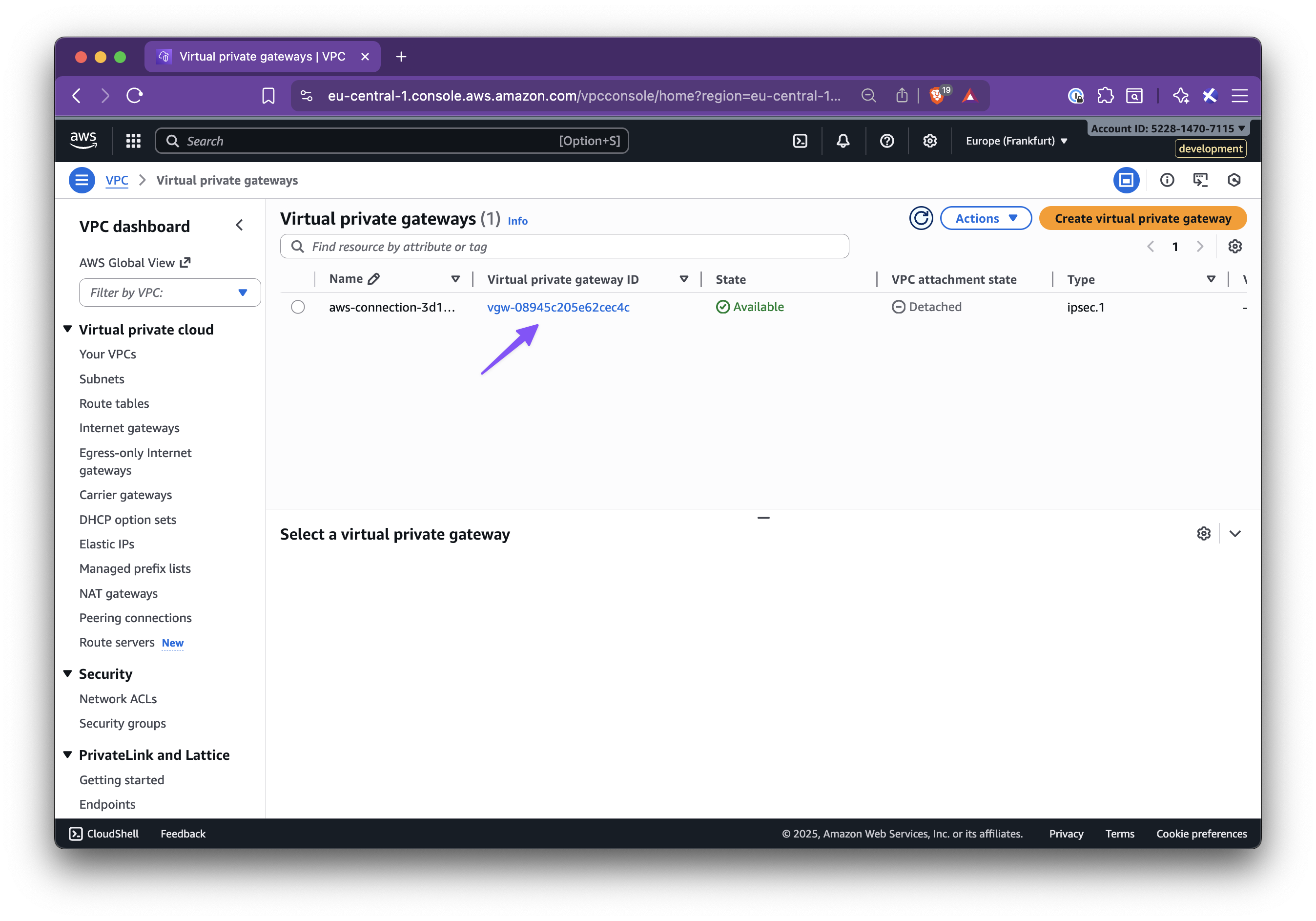
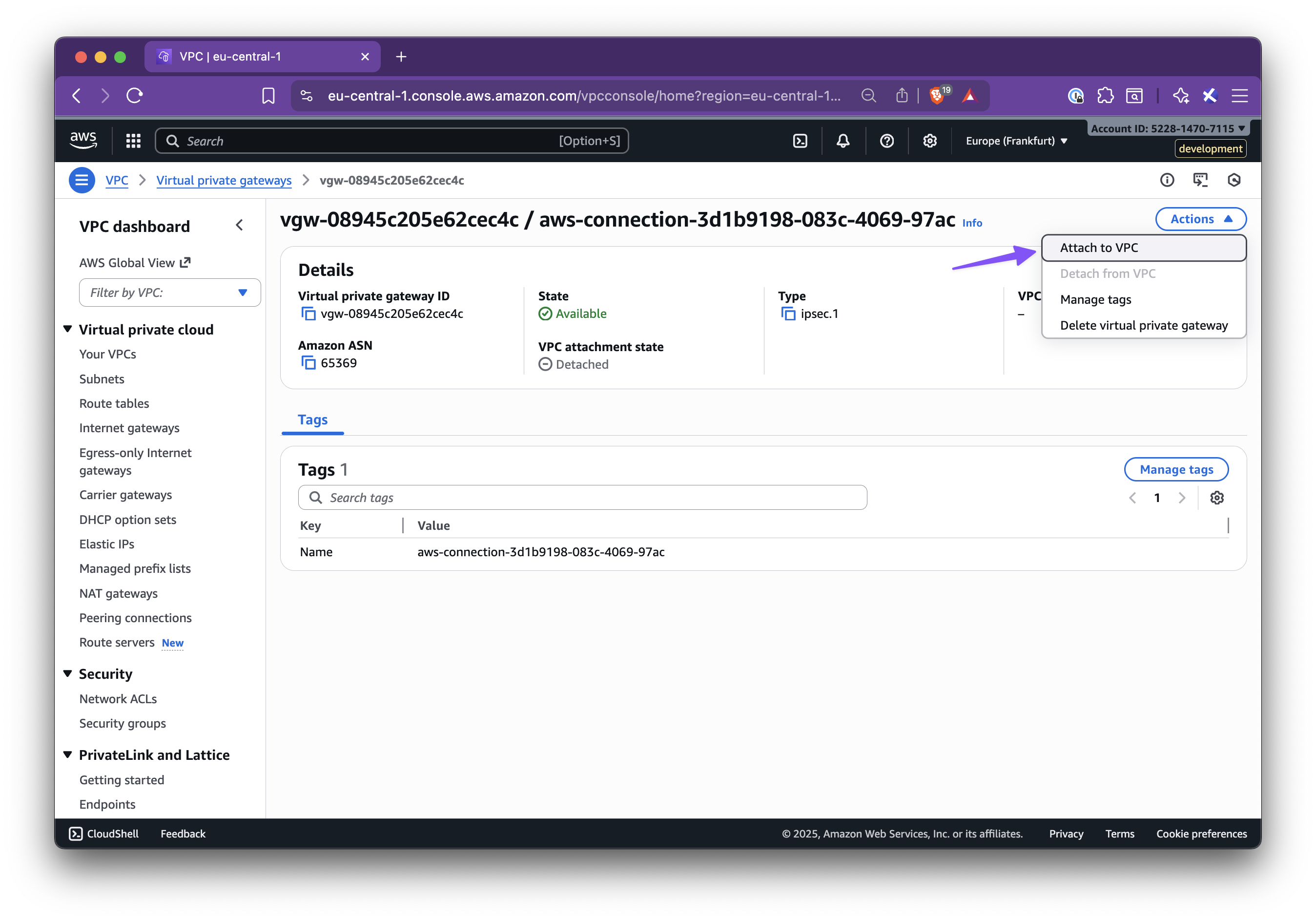
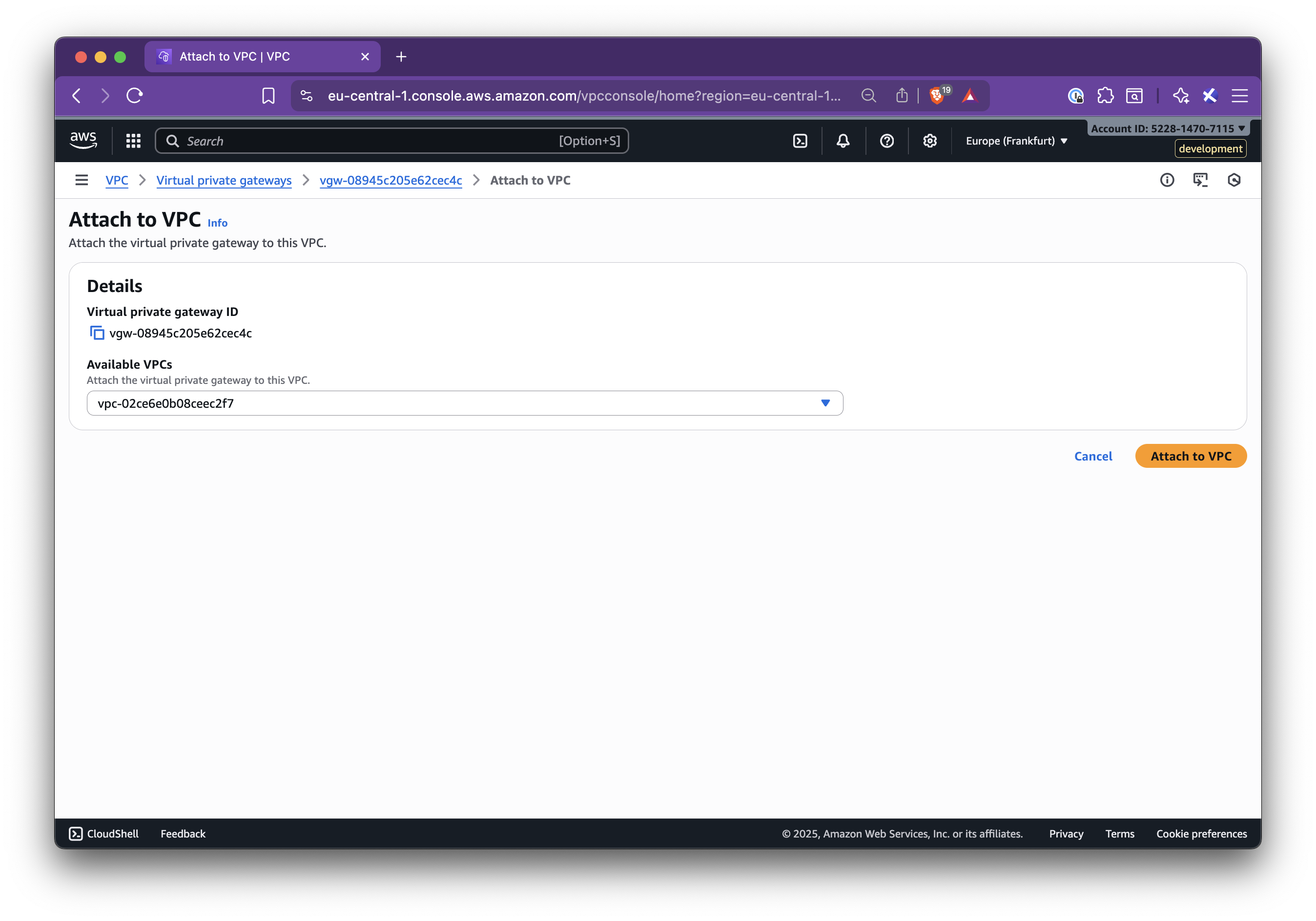
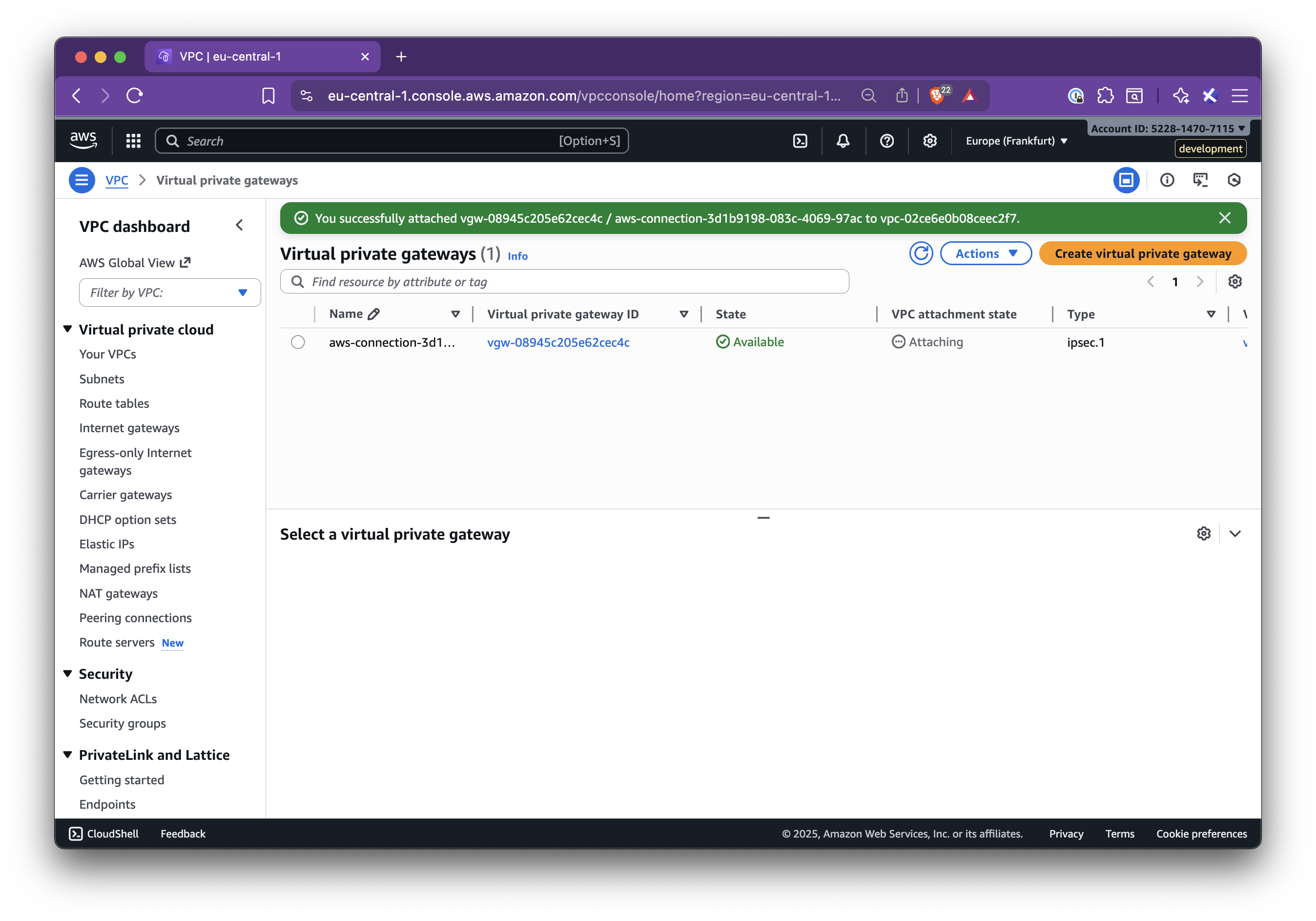
### Step 4.4: Add the Nirvana VPC CIDR to the AWS route table
1. Go to **AWS VPC → Route tables**
2. Select the route table for the target VPC
3. Click **Edit routes → Add route**:
- **Destination**: Nirvana VPC CIDR
- **Target**: the VGW from Step 4.2
4. Save changes
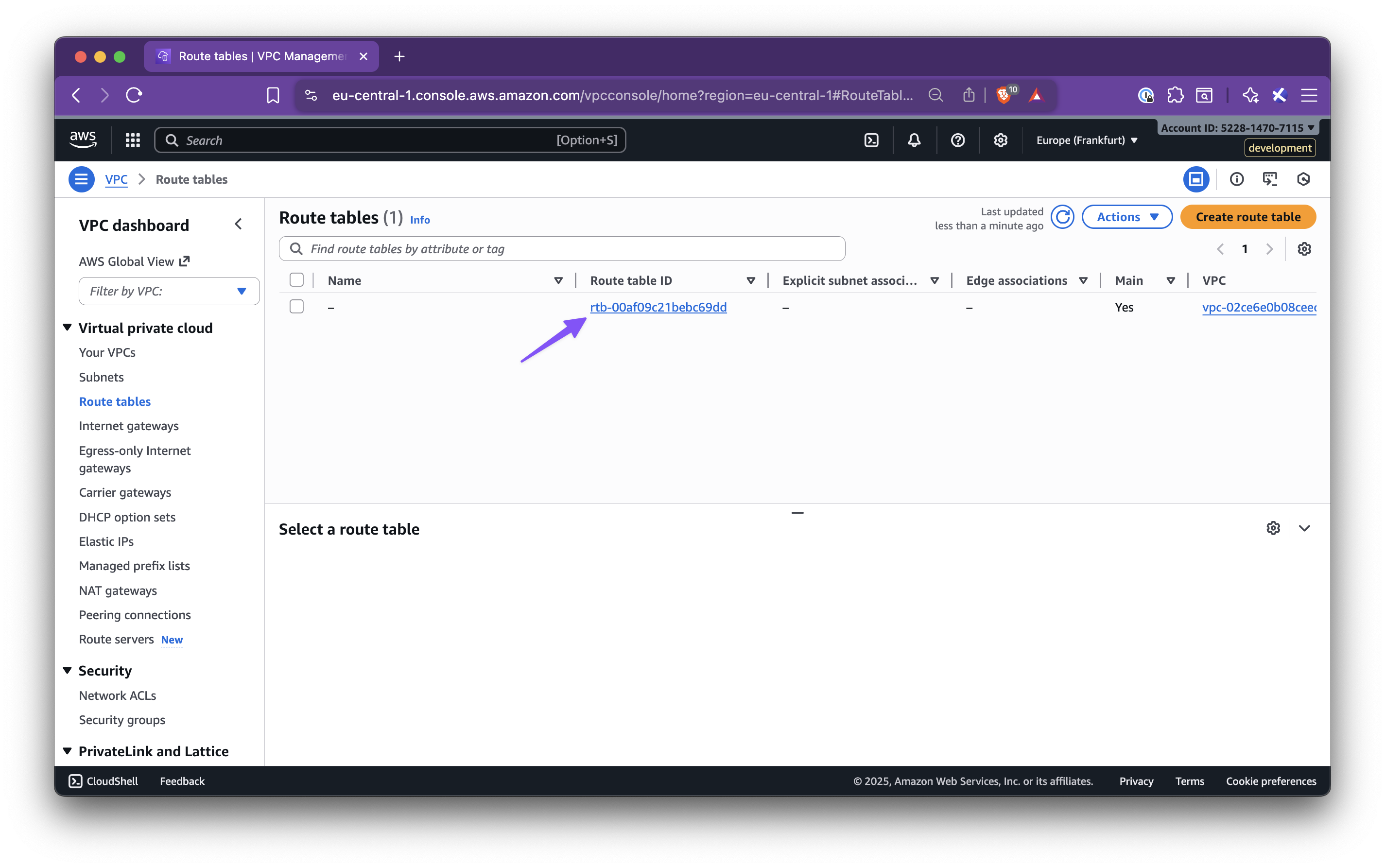
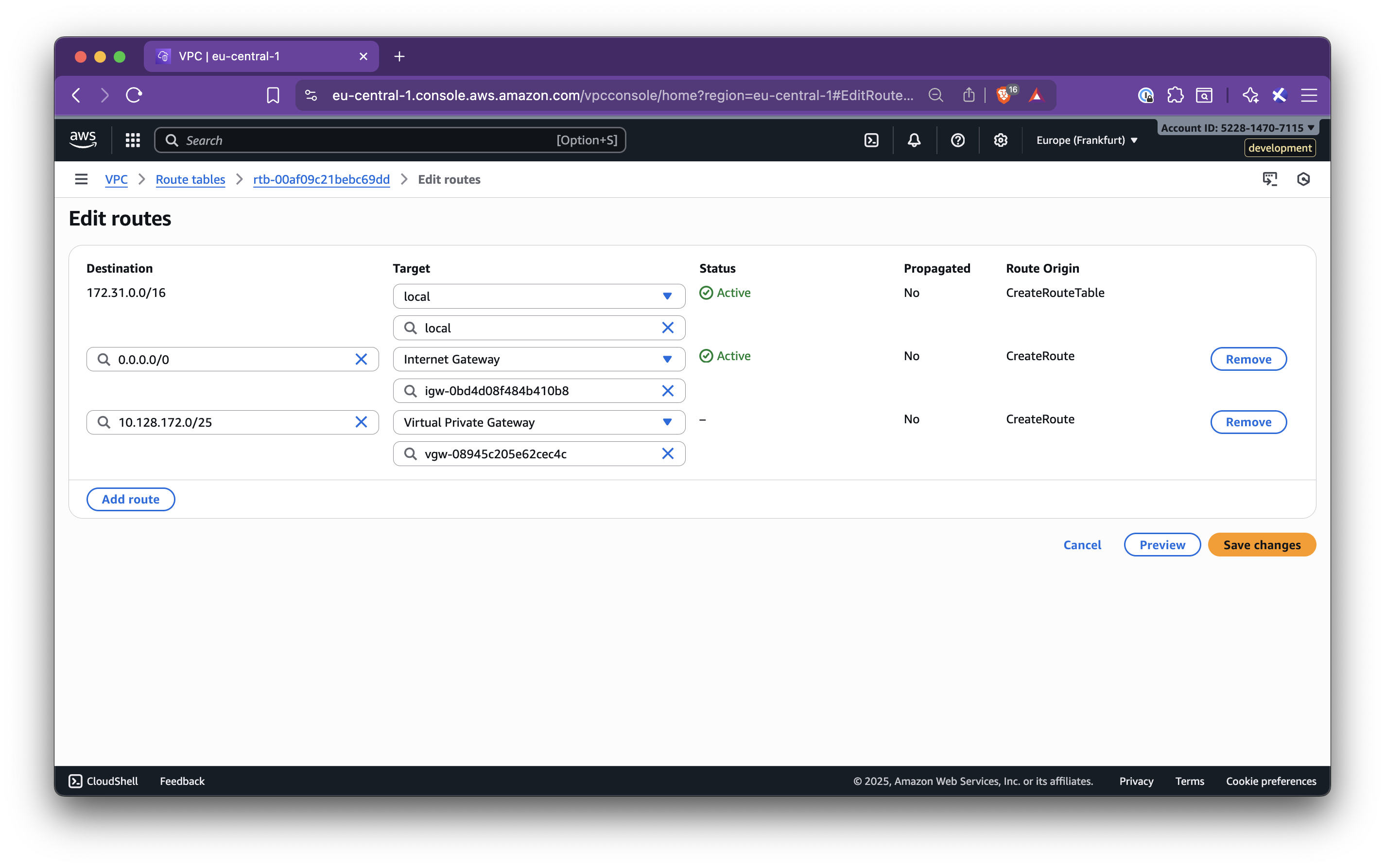
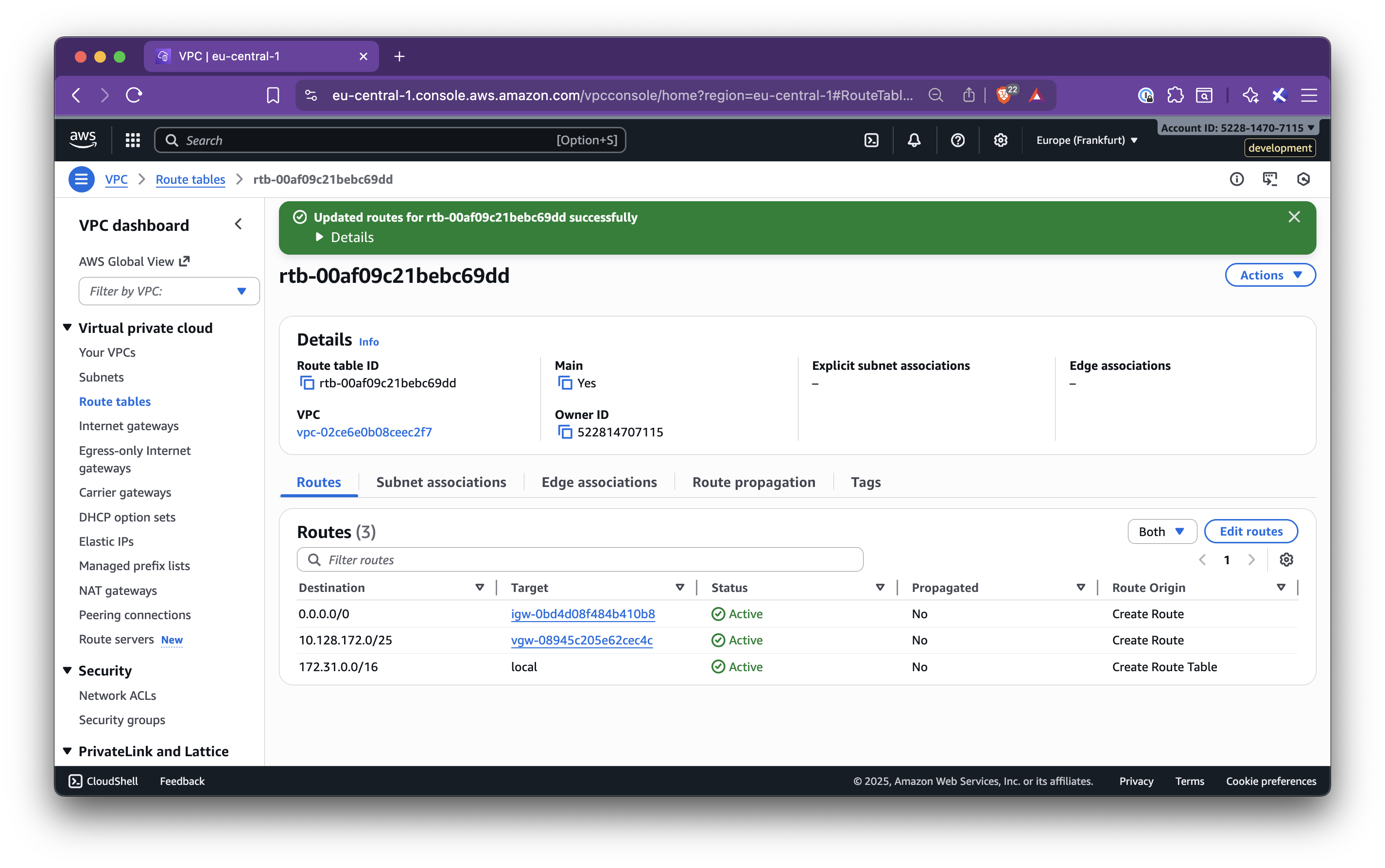
### Step 4.5: Create a Private Virtual Interface (VIF)
1. Go to **AWS Direct Connect → Connections**
2. Select the connection and click **Create virtual interface**
3. Configure the interface:
- **Type**: Private
- **Gateway type**: Virtual Private Gateway
- **Virtual interface name**: suggested from the panel
- **Virtual interface owner**: My AWS Account
- **Virtual Private Gateway**: the VGW attached
- **BGP ASN**: from the panel
- **Peer IPs and BGP Auth Key**: exactly as shown in the panel
4. Click **Create interface**
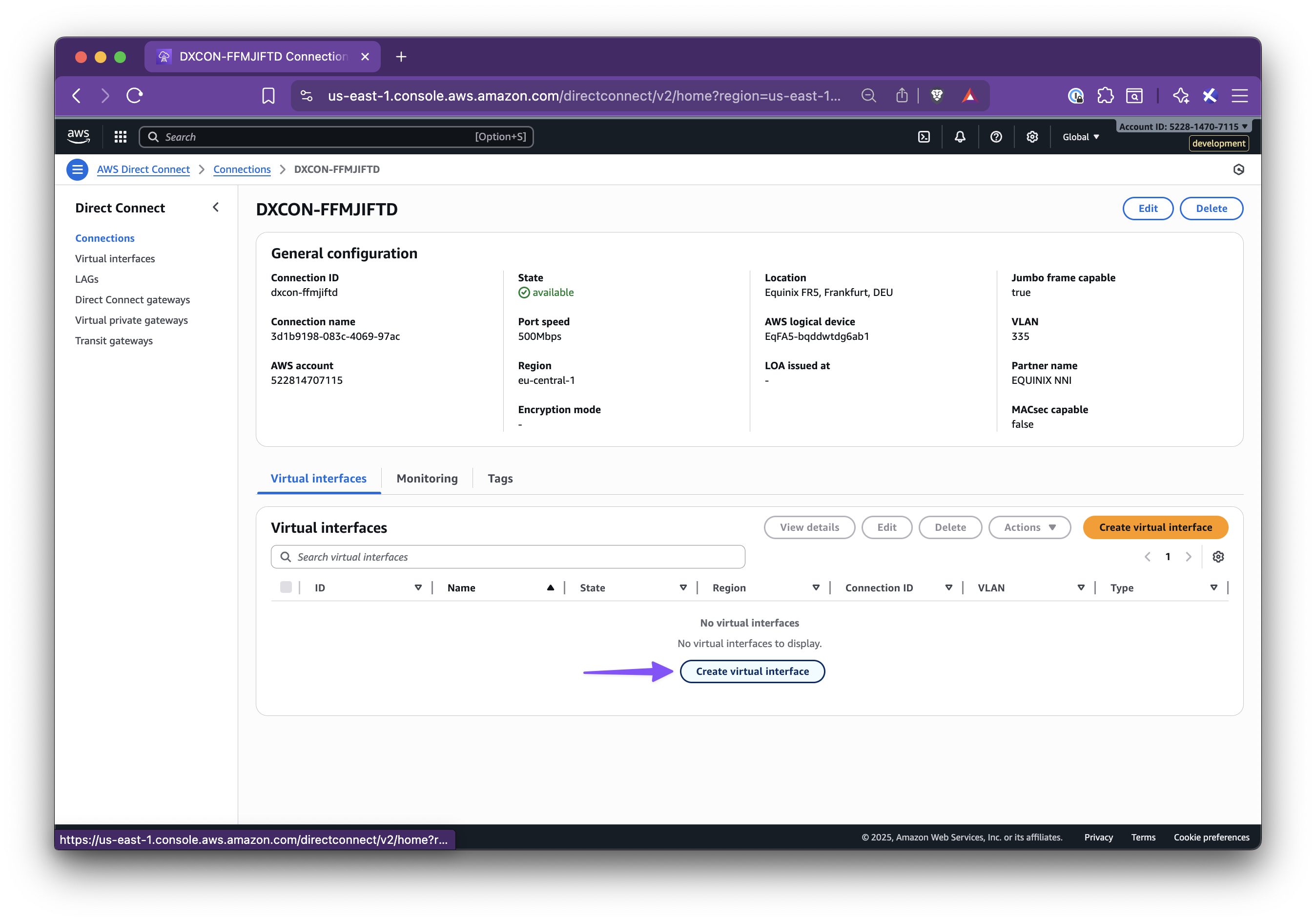
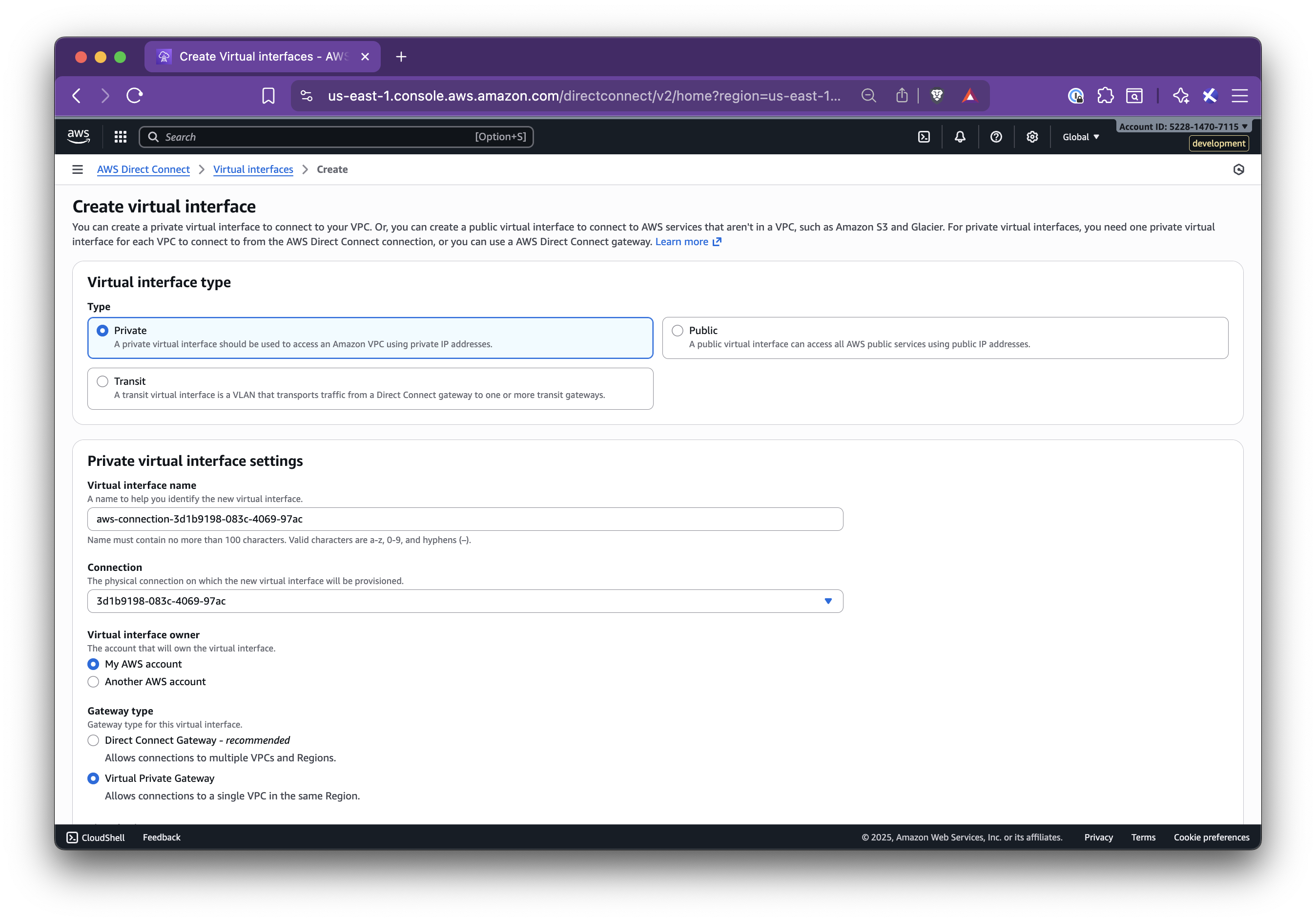
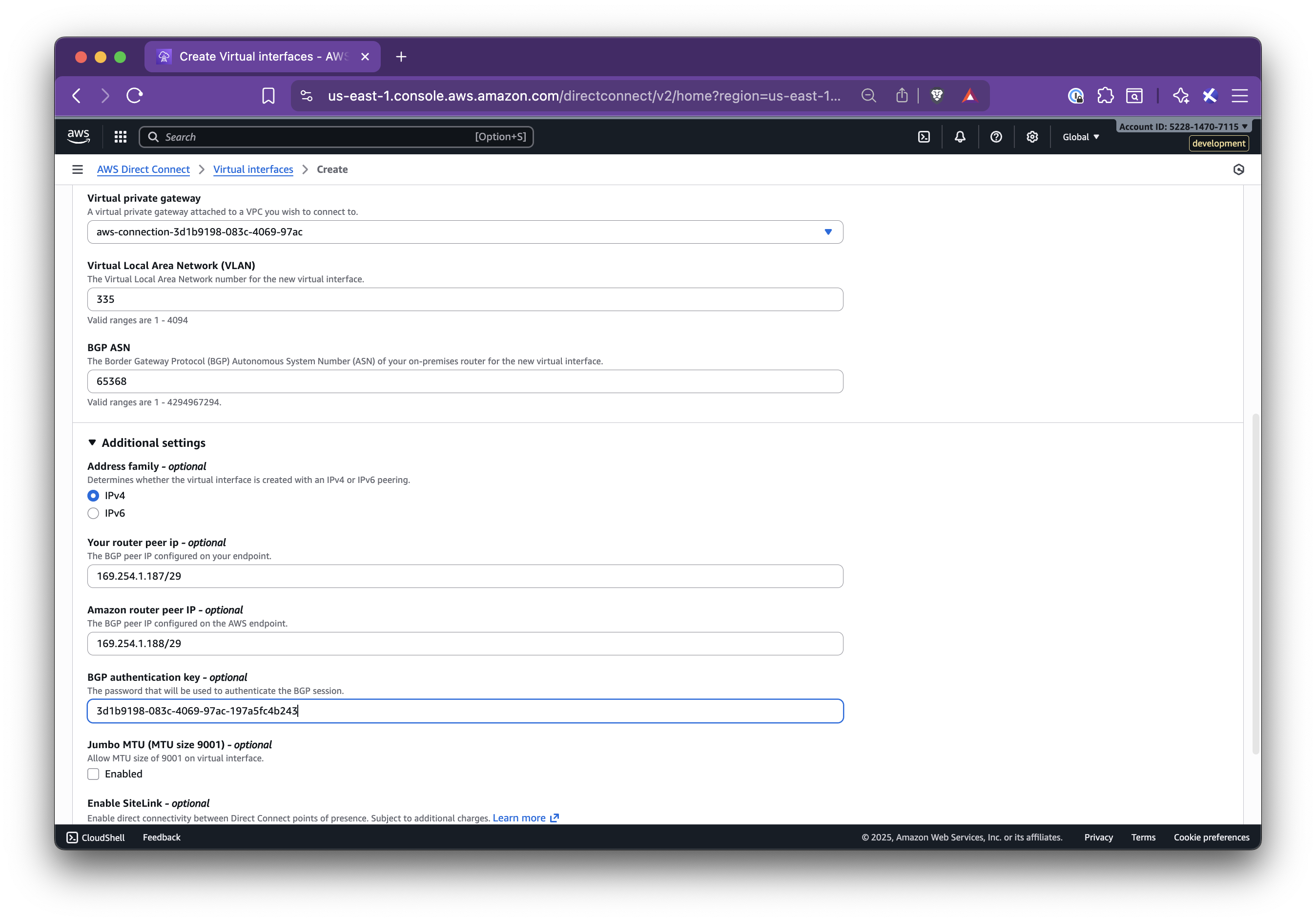
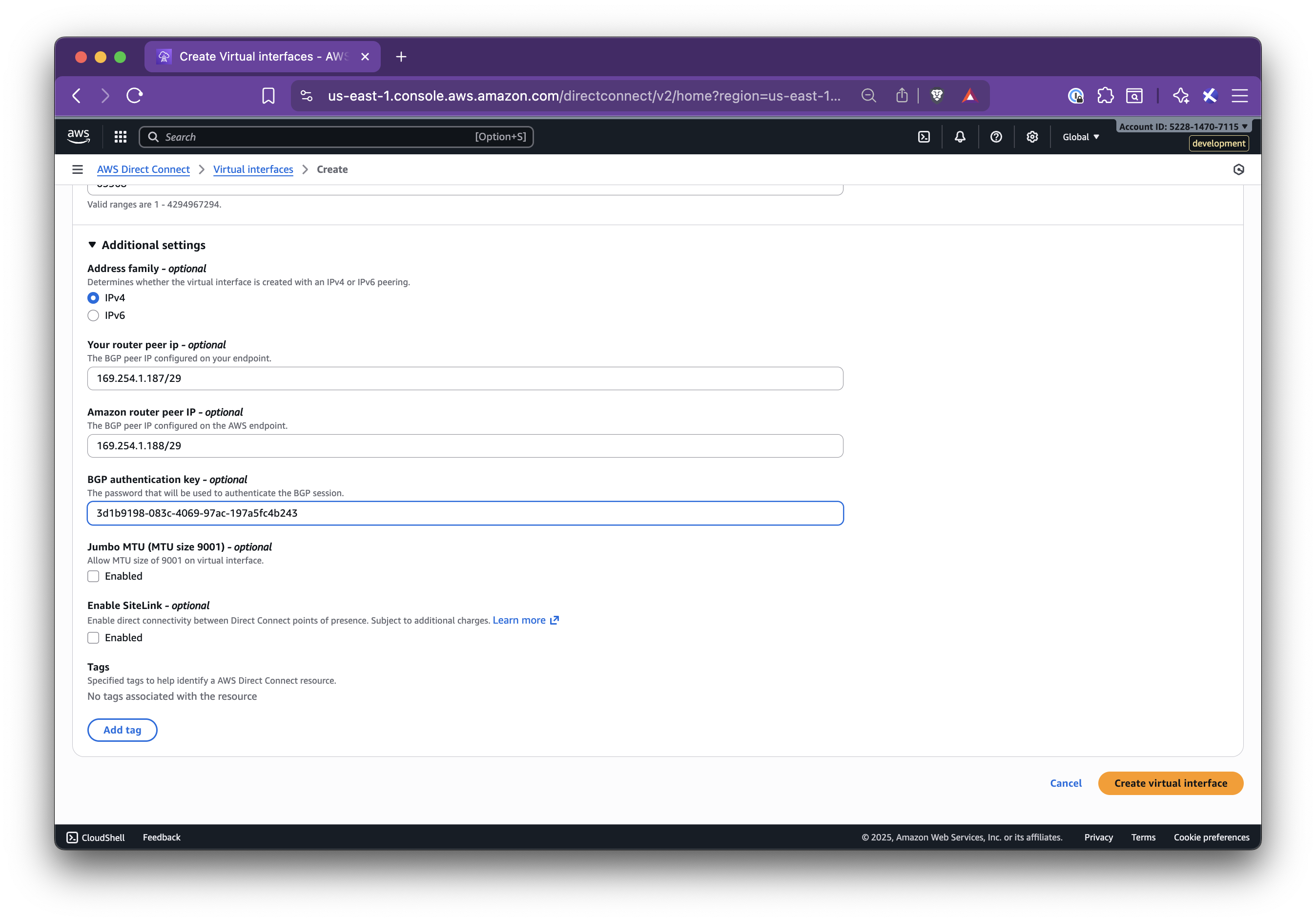
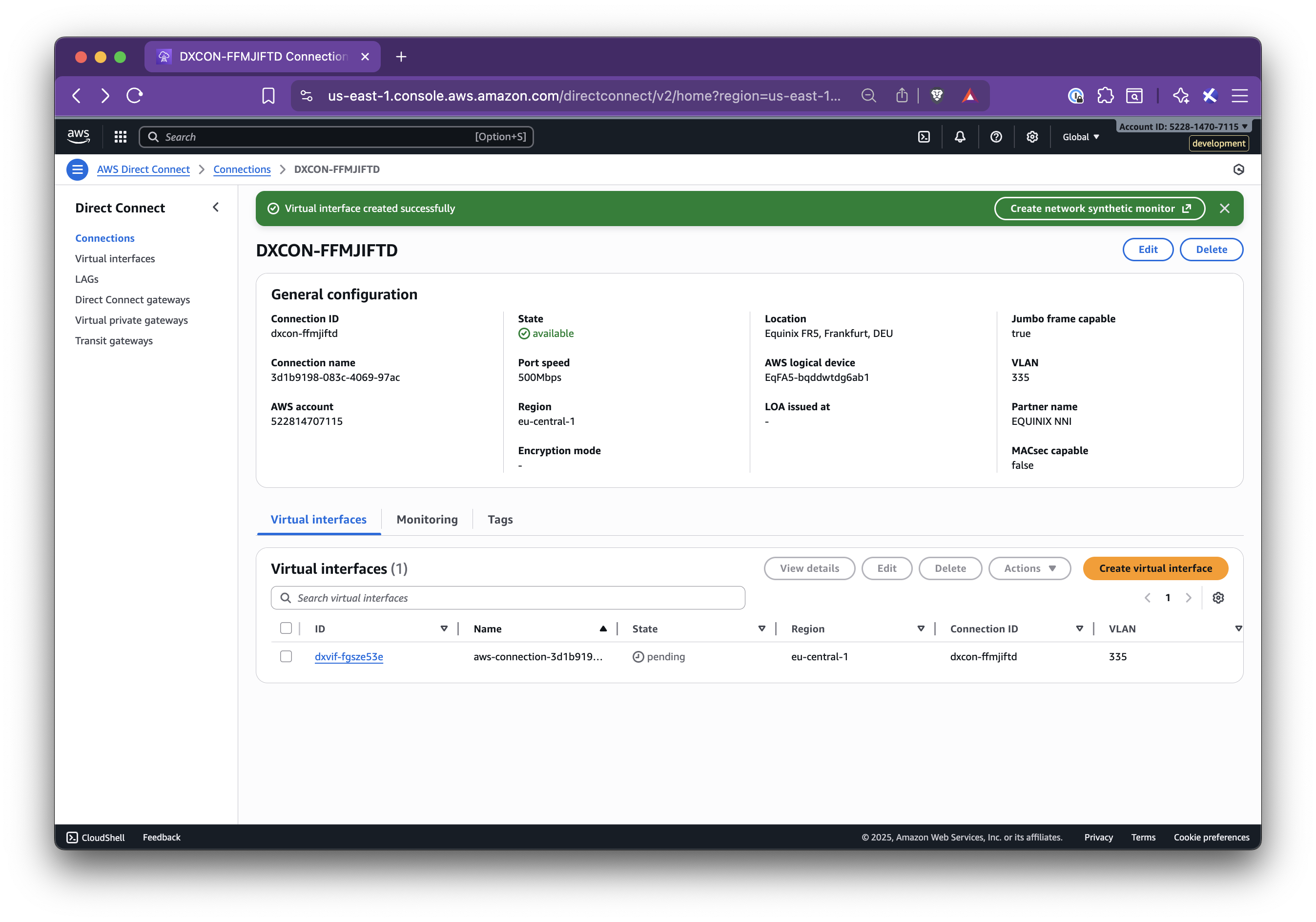
When the VIF is up, BGP will be established and the private link will be active.
## Step 5: Validate Connectivity
1. From an EC2 instance in the AWS VPC, test connectivity to resources in your Nirvana VPC CIDR (for example, by pinging or curling a private service)
2. From a Nirvana VM or Pod, test connectivity back to AWS resources
If connectivity fails, check:
- Route table entries (Nirvana CIDR to VGW)
- VIF status (BGP should be up)
- Security groups and NACLs on both sides
- Router IPs, ASNs, and BGP keys
Once traffic flows in both directions, your private connection between Nirvana and AWS is fully established! For additional support or troubleshooting, you can [reach out to our support team](https://nirvanalabs.io/contact).
:::note
You only need to add the Nirvana VPC CIDR route on the AWS side. The reverse route on Nirvana is handled automatically using the Provider CIDRs entered during connection creation.
:::
## Troubleshooting
- **VIF Down**: Check for incorrect BGP keys, mismatched ASNs, or reversed IP addresses
- **No Connectivity**: Confirm route table entries, security group rules, and that CIDRs are not overlapping
- **Stuck in Creating**: Open connection details and verify all values. Check VIF state in AWS
- **Edit**: Use the menu to edit Provider CIDRs or reopen the Setup steps if needed
---
title: IP Ranges
description: Nirvana Cloud’s IP Ranges
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/ips/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/ips/index.md
---
**Last Updated:** January 7, 2025
This page is the definitive source of Nirvana's current IP ranges.
From time-to-time, we will update this page to reflect the latest IP ranges.
## IPv4
Also available as a [IPv4 text list](/docs/cloud/networking/ips-v4.txt).
### us-sea-1
* 86.109.12.0/26
* 86.109.12.64/27
### us-sva-1
* 86.109.11.0/27
* 139.178.90.96/27
* 147.28.180.0/26
### us-sva-2
* 170.23.67.0/24
### us-chi-1
* 86.109.2.64/26
### us-wdc-1
* 147.28.163.0/26
* 147.28.228.224/27
### eu-frk-1
* 147.28.184.224/28
* 147.28.185.128/26
### ap-sin-1
* 147.28.178.128/26
### ap-tyo-1
* 136.144.52.128/26
---
title: Site-to-Site Mesh
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/site-to-site-mesh/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/site-to-site-mesh/index.md
---
Nirvana Cloud's Site-to-Site Mesh is a solution designed to establish secure, high-performance network connections across multiple locations. By leveraging WireGuard, a mesh network is created to allow direct communication between sites.
The Site-to-Site Mesh system offers a seamless networking experience, enabling resources across multiple sites to communicate as though they are in a single local network. This is particularly beneficial when managing geographically dispersed server locations or data centers as it allows for easy synchronization and sharing of data across these points.
In addition to securely and efficiently connecting multiple sites, the Site-to-Site Mesh offers the following advantages:
* **Performance**: The implementation of WireGuard offers high-speed secure connections, making the Site-to-Site Mesh suitable for substantial data transfers between various locations.
* **High Security**: With a mesh network, the communications between each location are securely encrypted, offering a more secure mode of communication compared to conventional methods.
* **Enhanced Reliability**: The use of WireGuard ensures that the Site-to-Site Mesh offers exceptional stability, maintaining reliable and available connections essential for modern, cloud-based operations.
Nirvana Cloud’s Site-to-Site Mesh solution provides a convenient way for businesses to meet multi-site networking requirements. This feature can facilitate reliable, secure, and high-performing communication channels across networks of diverse sizes and distribution.
---
title: Overview
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/vpcs/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/vpcs/index.md
---
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a digital network reminiscent of a conventional network managed in a physical data center.
### Subnets
A subnet denotes a spectrum of IP addresses in your VPC, designed to be user-friendly and region-centric. A single-subnet model per VPC simplifies VPC management and adoption.
### Public IP Addresses
Instances that need to connect to the internet or be accessed from the internet will need a public IP address. Within the cloud setup, users are offered the benefit of allocating a static public IP address to their instances. Unlike dynamic IP addresses, a static public IP address does not change due to stop/start instances. This constancy ensures stable, easy, and more dependable access to applications or services running on the specific instance.
### Firewall Rules
In the architecture of a VPC, firewall rules are pivotal for maintaining data security. These rules offer stateless filtering controls that govern whether network traffic should be allowed or denied. These permissions or denials are based on criteria like the IP protocol, source IP, and designated port numbers.
Firewall rules help encrypt all traffic that enters or exits the VPC, strengthening protection against unapproved access and potential data breaches. They also ensure compliance with all necessary organizational policies, regulations, and requirements, increasing the reliability and trustworthiness of the virtual environment.
It's important to note that the network within a VPC is engineered in a way that allows all virtual machines to automatically communicate with each other. For connections between VMs outside the VPC or with the public internet, specific destination IPs and required ports must be manually defined within the VPC security list for the appropriate routing and connection.
---
title: FAQ
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/vpcs/faq/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/vpcs/faq/index.md
---
---
title: Firewall Rules
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/vpcs/firewall-rules/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/networking/vpcs/firewall-rules/index.md
---
Firewall rules are used to control inbound traffic to your network, thus ensuring the security and integrity of your application or service by defining which kind of traffic is allowed and from where.
---
title: Nirvana Kubernetes Service (NKS)
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/nks/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/nks/index.md
---
Nirvana Kubernetes Service (NKS) is a fully managed Kubernetes service designed to streamline the deployment and management of containerized applications on Nirvana Cloud. By leveraging NKS, organizations can efficiently handle the complexities of Kubernetes while focusing on their core applications and services.
**Importance of Kubernetes in the Web3 Industry**
Kubernetes is essential in the Web3 industry, particularly for the deployment of decentralized applications (dApps), data ingestion pipelines, decentralized exchanges (DEXes), and other blockchain-related services. Its capabilities in orchestration, scaling, and management of containerized workloads make it a crucial tool for ensuring the reliability, security, and performance of Web3 applications.
**Web3 Use Cases for NKS**
* Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Platforms: DeFi platforms, such as lending platforms, yield farming, and synthetic asset issuance, leverage NKS for secure, scalable, and reliable infrastructure.
* Non-Fungible Token (NFT) Marketplaces: NFT marketplaces require robust infrastructure to handle large volumes of transactions and data. NKS provides the necessary scalability and reliability.
* Smart Contract Development and Testing: NKS enables the creation of isolated environments for the development and testing of smart contracts. These environments can be easily replicated and scaled.
* Decentralized Applications (dApps): Deploy and manage dApps efficiently using NKS, benefiting from its scalability and security features.
* Blockchain Data Analytics: Analyzing blockchain data requires processing large datasets, which can be efficiently managed using NKS. NKS can host analytics tools and data pipelines to process and analyze blockchain data.
**Why choose NKS?**
* Fully Managed: NKS is a fully managed Kubernetes service where the Nirvana Labs team handles all aspects of cluster creation, upgrades, and maintenance. This allows customers to concentrate on building and deploying their applications without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure.
* Purpose-Built for Web3: NKS is specifically designed for Web3 applications. Built on Nirvana Cloud, it provides a secure and scalable environment tailored to the unique requirements of Web3 services, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
* Scalable: NKS offers a highly scalable platform that can adapt to the changing needs of your business. Customers can easily scale their clusters by adding or removing worker nodes or pools as their resource requirements evolve.
**NKS Components**
* Clusters: A cluster is a fundamental unit in Kubernetes, consisting of a set of nodes that run containerized applications. Each cluster includes a controller node that manages the cluster operations and worker nodes that execute the applications.
* Controller Nodes: The controller node is responsible for running the Kubernetes control plane, which manages the cluster and schedules applications on the worker nodes. This node is fully managed by the Nirvana Team, and customers are not billed for it.
* Worker Node Pools: Worker node pools are groups of worker nodes with identical configurations. These pools enable customers to organize their worker nodes according to specific resource requirements, facilitating efficient management and scaling.
* Worker Nodes: Worker nodes are the nodes within a cluster that run the containerized applications. Managed by the controller node, these worker nodes are part of a worker node pool. Customers are billed for the resources consumed by the worker nodes, allowing for cost-effective scaling based on actual usage.
---
title: Clusters
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/nks/clusters/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/nks/clusters/index.md
---
Kubernetes clusters are widely used in the cloud industry to deploy and manage containerized applications. This removes the need for customers to manage the underlying infrastructure, allowing them to focus on building and deploying their applications.
**Cluster Creation**: Customers can create clusters with just a few clicks through the Nirvana Cloud Dashboard or API. This streamlined process reduces the complexity and time associated with setting up Kubernetes clusters.
**Configuration Options**: When creating a cluster, customers have the flexibility to choose various settings to match their specific requirements:
* Region Selection: Customers can select the geographic region where the cluster will be deployed, ensuring proximity to their workloads and compliance with regional regulations.
* Worker Node Pool Configuration: Customers can define the configuration for worker node pools, including the amount of CPU, RAM, and storage of the worker nodes.
* Number of Worker Nodes: Customers can specify the initial number of worker nodes in each pool, allowing them to start with the resources they need and scale up or down as required.
* Kubernetes Version: Customers can select the desired Kubernetes version, ensuring compatibility with their applications and taking advantage of the latest features and security updates.
* Additional Settings: Other settings such as network policies, storage options, and access controls can be configured to meet the specific needs of the applications and organizational policies.
**Scalability**: NKS allows customers to easily scale their clusters by adding or removing worker nodes or entire node pools based on their resource requirements. This dynamic scaling ensures that the cluster can handle varying workloads efficiently without over-provisioning resources.
**Managed Operations**: The Nirvana Team handles the underlying operations and maintenance of the controller nodes which are the brains of the cluster. This fully managed approach ensures that the clusters are always running optimally and securely, with minimal intervention from the customer.
**Deployment Ease**: Deploying applications on NKS clusters is straightforward. Customers can use Kubernetes manifests, Helm charts, or other deployment tools to manage their applications. NKS integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, enabling automated deployments and updates.
By leveraging NKS for their Kubernetes clusters, customers can achieve a high degree of operational efficiency, scalability, and reliability, allowing them to focus on innovation and delivering value to their users.
---
title: Controller Nodes
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/nks/controller-nodes/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/nks/controller-nodes/index.md
---
Controller nodes are the brain of the Kubernetes cluster, performing critical functions that ensure the cluster operates efficiently and reliably.
**Key Functions of Controller Nodes**
* Kubernetes Control Plane: Controller nodes run the Kubernetes control plane, which manages the overall state of the cluster and schedules applications on worker nodes. This includes tasks such as load balancing, scaling, and maintaining the desired state of the applications.
* etcd Database: The controller nodes run the etcd database, which is a distributed key-value store used to persist the cluster's state. This database stores all cluster configuration data and ensures consistency across the cluster.
* Kubernetes API: The Kubernetes API server runs on the controller nodes, providing a RESTful interface for interacting with the cluster. This allows customers to use tools like kubectl, Helm, and other Kubernetes tooling to manage their applications and cluster resources.
**Managed with ❤️ by the Nirvana Team**
The controller nodes are completely managed by the Nirvana Team. This means that Nirvana Cloud handles all aspects of their operation, including maintenance, updates, and monitoring. Customers do not need to worry about the complexities of managing the control plane infrastructure.
Customers are not billed for controller nodes, which are provided as part of the NKS service. This makes it cost-effective for customers to leverage the full capabilities of Kubernetes without incurring additional costs for control plane management.
**Configuration Options**
* Single Controller Node: Customers can choose a single controller node configuration for their cluster. This option is suitable for development, testing, and smaller production environments where high availability is not a critical requirement.
* Highly Available Configuration: For production environments that require high availability and fault tolerance, customers can opt for a highly available controller node configuration. This setup runs three controller nodes, ensuring that the cluster remains operational even if one or two controller nodes fail. This redundancy is crucial for maintaining continuous availability and resilience against failures.
By providing robust and fully managed controller nodes, NKS ensures that customers can focus on deploying and managing their applications with confidence, knowing that the critical aspects of cluster management are handled by the Nirvana Team.
---
title: Node Pools
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/nks/worker-node-pools/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/nks/worker-node-pools/index.md
---
Node pools are a set of worker nodes that share the same configuration, enabling efficient management and scaling of resources based on application requirements.
**Key Features of Node Pools**
* Resource Grouping: Node pools allow customers to group worker nodes according to their resource requirements. This organizational strategy ensures that similar types of workloads are run on nodes with appropriate configurations.
* Multiple Configurations: Customers can create multiple node pools with different configurations to support various types of applications within the same cluster. This flexibility ensures optimal resource utilization and performance.
**Configuration and Scalability**
* Cluster Creation: When creating a cluster, customers can specify the worker node pool configuration, including the number of worker nodes in each pool and other relevant settings. This initial setup can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the applications being deployed.
* Dynamic Scaling: Customers can easily scale their clusters by adding or removing worker nodes or entire node pools based on their resource requirements. This dynamic scaling capability allows for efficient resource management and cost control.
**Optimization for Specific Workloads**
* Compute-Intensive Workloads: For applications that require significant computational power, customers can create node pools with high CPU worker nodes. This ensures that compute-intensive workloads have the necessary resources for optimal performance.
* Memory-Intensive Workloads: Applications that require large amounts of memory can be assigned to node pools with high memory worker nodes. This configuration is ideal for workloads such as large-scale data processing or in-memory databases.
* Storage-Intensive Workloads: For stateful applications that require substantial storage, customers can create node pools with nodes that have large storage capacities. This setup ensures that storage-intensive workloads have sufficient space and performance capabilities.
**Simplified Management**
With node pools, customers can manage and scale their clusters efficiently without the need to handle individual worker nodes. This abstraction simplifies cluster management and allows customers to focus on application performance and resource optimization.
By leveraging the capabilities of node pools, customers can ensure that their Kubernetes clusters are optimized for diverse workloads, providing a robust and flexible environment for deploying and managing containerized applications.
---
title: Worker Nodes
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/nks/worker-nodes/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/cloud/nks/worker-nodes/index.md
---
Worker nodes are the backbone of a Kubernetes cluster, responsible for running the actual workloads. These nodes host the containers that constitute the applications deployed on the cluster.
**Key Functions of Worker Nodes**
* Application Execution: Worker nodes run the containers that make up the applications, handling the actual processing, storage, and networking tasks required by the applications.
* Management by Controller Nodes: Controller nodes oversee worker nodes by scheduling applications to run on them, monitoring their health, and managing their lifecycle. This ensures efficient use of resources and high availability of applications.
**Configuration and Deployment**
* Worker Node Pool Configuration: When creating a cluster, customers define the configuration of worker node pools. This configuration includes several critical settings:
* Instance Type: Specifies the type of virtual machine or physical hardware to be used for the worker nodes, impacting performance and capacity.
* Number of Worker Nodes: Defines the initial number of worker nodes in the pool, determining the cluster's capacity to handle workloads.
* Disk Size: Sets the storage capacity available on each worker node, ensuring sufficient space for the containers and their data.
* Other Settings: Includes additional configurations such as networking, security policies, and resource limits to tailor the nodes to specific application needs.
By carefully configuring worker node pools and leveraging the robust management capabilities of NKS, customers can ensure that their applications run efficiently and reliably on a scalable and flexible Kubernetes infrastructure.
---
title: Docs Directory
description: Browse all Nirvana Labs documentation
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/directory/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/directory/index.md
---
import { Card, CardGrid, LinkCard } from '@astrojs/starlight/components';
## Cloud
## Blockchain
## Resources
---
title: FAQ
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/faq/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/faq/index.md
---
## About Nirvana Labs
### Q: What is Nirvana Labs?
A: Nirvana Labs is a high-performance bare-metal cloud purpose-built for Web3. It delivers ultra-low-latency compute, elastic block storage, and private fiber networking for sequencers, validators, routers, and intent execution engines.
---
### Q: What makes Nirvana different from AWS or GCP?
A: Hyperscalers were designed for web workloads — Nirvana is built for real-time, high-throughput blockchain execution.
- Dedicated bare metal (no noisy neighbors)
- Lightweight hypervisor (no virtualization latency)
- Hyper-converged architecture (dedicated compute + storage + networking unified)
- Private routing via Nirvana Connect
- Deterministic performance at lower cost
---
### Q: Where are your data centers?
A: Nirvana operates globally with coverage in North America, Europe, and Asia — positioned near major chain hubs for ultra-low-latency connectivity.
We leverage 6 **data centers** in Silicon Valley, Chicago, Washington, D.C., Frankfurt, Tokyo, and Singapore.
---
### Q: Who uses Nirvana today?
A: **Over 50+ teams** use Nirvana for their mission-critical blockchain infrastructure — including Aori, BitGo, Chainlink, Fireblocks, Nansen, RedStone, Keyrock, and Goldsky.
These teams run high-performance workloads such as **routing engines, intent execution, indexing, validation, and settlement** on Nirvana Cloud.
Nirvana also **supports 60+ blockchain networks** across L1s, L2s, appchains, and testnets — enabling global deployments and elastic scaling for multi-chain infrastructure.
---
### Q: Are you SOC audited?
A: Yes — Nirvana Labs is **SOC 2 Type II compliant**.
---
### Q: What kind of implementation support do you provide?
A: We provide **Slack channel onboarding** with engineers across regions to assist you through the entire setup.
---
### Q: How do I get in touch?
Ready to Get Started? [**Get in touch**](https://nirvanalabs.io/contact?ref=blog.nirvanalabs.io) and we'll help you get set up with Nirvana.
**Learn more at**
[Nirvana](https://nirvanalabs.io/) | [Blog](https://blog.nirvanalabs.io/) | [Docs](https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/nodes/getting-started-with-nirvana-labs?ref=blog.nirvanalabs.io) | [Twitter](https://x.com/nirvanalabsai?ref=blog.nirvanalabs.io) | [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/company/nirvana-labs-ai?ref=blog.nirvanalabs.io)
---
## Product - General
### Q: What is the Nirvana Cloud stack?
A: Nirvana provides dedicated bare-metal infrastructure with built-in compute, storage, networking, orchestration, and dedicated RPC nodes — designed specifically for blockchain performance and cost efficiency.
*A Web3-native cloud stack built for performance*
**L0 · Compute** — Bare metal speed with cloud flexibility. Built on latest AMD chips with high clock speeds. Lightweight hypervisor with minimum overhead. Run workloads along nodes for ultra-low latency.
**L1 · Storage** — High-performance, crypto-tuned block storage built for always-hot blockchain data with sustained IOPS. 20,000 baseline IOPS, up to 600,000 burst IOPS. Sub-millisecond latency.
**L2 · Networking** — Private connectivity that keeps Web3 data transfer off the public internet with no egress cost. Global private fiber across major crypto hubs. Direct routing between Nirvana and other clouds.
**L3 · Orchestration** — A Kubernetes service built to deploy and scale Web3 workloads in seconds.
**L4 · Dedicated RPC Nodes** — Reliable, ultra low-latency RPC nodes across 90+ networks with custom configs, node continuity, and full hardware + software control.
---
### Q: What is bare metal cloud?
A: Bare metal cloud is a cloud computing model that gives you access to **dedicated physical servers,** not shared or virtualized machines. Unlike traditional cloud (e.g., Amazon Web Services or Google Cloud Platform), where workloads run on a shared hypervisor, bare metal gives you **full control of the entire server** - CPU, memory, storage, and networking - with no noisy neighbors or virtualization overhead.
---
### Q: What’s special about your bare metal cloud?
- No shared tenancy or heavy virtualization
- Low-jitter, deterministic performance
- Private routing backbone
- Fast provisioning (under 30 seconds)
- Transparent, linear pricing
Nirvana gives you the performance of a private data center without the overhead.
---
### Q: What is a hypervisor?
A: A hypervisor is a thin software layer between the physical server and the operating system. It lets you provision, isolate, and manage workloads on the same machine.
Two main types:
- Type 1 (bare metal) — runs directly on the hardware, fast and secure.
- Type 2 (hosted) — runs on top of an OS, adding more overhead.
**Hyperscalers** use **large, multi-tenant Type 1 hypervisors** to carve up one physical server into many virtual machines for different customers. That model is efficient for them, but the shared infrastructure introduces **scheduling delays, virtualization bloat, and performance jitter** — especially under load.
**Nirvana Labs** also uses **Type 1**, but **single-tenant**. Each machine is fully yours — no other workloads compete for resources. The hypervisor is **ultra-thin** and used only for provisioning, isolation, and automation, not sharing.
---
### Q: What’s special about Nirvana’s hypervisor?
A: Nirvana’s hypervisor is a **very thin, single-tenant Type 1 layer** designed specifically for Web3 workloads.
While hyperscalers use **large multi-tenant hypervisors** to share infrastructure — adding overhead, noisy neighbors, and unpredictable performance — Nirvana gives each customer a **dedicated machine** with near-zero overhead and deterministic control.
What makes it special:
- **Single-tenant architecture:** No resource contention or noisy neighbors.
- **Ultra-lightweight:** Near-zero overhead, no multi-tenant bloat.
- **Performance-optimized:** Tuned for high-CPU blockchain workloads (e.g., sequencers, validators, indexers).
- **Hyper-converged design:** Compute, storage, and networking unified for predictable low latency.
- **Custom drivers and networking:** Engineered to minimize jitter and maximize IOPS.
- **Deterministic control:** You get root access and full machine performance, while the hypervisor quietly handles provisioning, isolation, and automation.
👉 In short: **single-tenant, bare-metal performance** with cloud-grade flexibility without hyperscaler trade-offs.
---
### Q: Why do you call it a bare metal cloud if there’s a hypervisor?
A: Most “bare metal” providers today run a lightweight control layer; and so do we.
The key difference is **how the hypervisor is used**:
Traditional hyperscalers run **heavy, multi-tenant hypervisors** designed to share infrastructure across many customers.
Nirvana uses a **very thin, single-tenant hypervisor** that sits directly on the physical server. It isn’t used to share resources between unrelated tenants; it’s there to give you full control of the machine with **near-zero overhead**.
This design preserves **true bare-metal performance** while adding the flexibility of clean provisioning, isolation, and automation without compromising the core benefits of dedicated infrastructure.
---
### Q: How are compute, storage, and networking handled?
A: Nirvana uses a **hyper-converged architecture**, meaning compute, storage, and networking are integrated into a single stack rather than split into siloed services. This design eliminates many of the bottlenecks common in traditional cloud setups.
- **Low-latency compute:** Workloads run on dedicated bare metal servers located near major chain hubs. No multi-tenancy means no noisy neighbors, ensuring deterministic performance even at peak traffic.
- **Elastic block storage:** Our high-performance NVMe-based storage fabric scales with your workload. It’s optimized for sustained blockchain throughput, giving you fast, reliable data access without shared resource contention.
- **Private networking with Nirvana Connect:** Instead of routing over the public internet, traffic flows through a private, low-jitter backbone that connects directly to other major clouds and partners. This dramatically reduces latency and egress costs while improving stability.
- **End-to-end consistency:** Because everything runs on the same node and backbone, throughput stays stable under heavy load — ideal for execution workloads like sequencers, validators, routers, and indexers.
Nirvana removes the layers that slow Web3 workloads down delivering **bare-metal performance**, **elastic scaling**, and **private network reliability** in one stack.
---
### Q: How fast can I deploy infrastructure on Nirvana?
A: Typically **under 30 seconds**. You can deploy clusters near chain hubs, scale quickly, and maintain predictable performance.
---
### Q: How does Nirvana handle monitoring and uptime?
A: Observability is native:
- Real-time performance monitoring
- Built-in alerting & scaling
- Failover and self-healing clusters
---
### Q: What's the difference between Archive Node, Full Node, Light Node, and Dedicated Node?
- **Archive Node** — Stores the entire blockchain history, including all historical states and blocks.
- **Full Node** — Maintains the current blockchain state and validates all blocks and transactions.
- **Light Node** — Stores only block headers and relies on full nodes to retrieve detailed data.
- **Dedicated Node** — A full or archive node allocated exclusively to one customer, with guaranteed performance and resources.
---
### Q: How do you handle data delivery and RPC traffic?
A: Nirvana runs its own **proprietary CDN** and **unified API gateway**, co-located with compute and storage.
- No Cloudflare/Fastly dependency
- Custom routing and caching
- Dedicated node pools
- Programmable routing for sequencers, validators, and indexers
- Linear pricing with no per-request bloat
---
### Q: Do you support Kubernetes?
A: Yes. You can spin up your own Kubernetes cluster (like EKS) on Nirvana today.
**Nirvana Kubernetes Service (NKS)** — our fully managed Kubernetes offering — is currently **in development** and will be available soon.
---
### Q: How does Nirvana compare to hyperscalers?
| Category | Hyperscalers | Nirvana |
| --- | --- | --- |
| Infra | Shared + virtualized | Bare metal, private |
| Architecture | Siloed layers | Hyper-converged |
| Provisioning | Slow & complex | Fast, deterministic |
| Observability | Add-on tooling | Built-in |
| Routing | Public internet | Private backbone |
| Pricing | Per GB / per request | Transparent, linear |
| Fit for Web3 | Retrofitted | Purpose-built |
---
title: Glossary
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/glossary/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/glossary/index.md
---
## Archive Node
A specialized full node that stores every historical blockchain state at each block. Unlike standard full nodes, archive nodes enable deep historical queries — such as past balances, contract states, and storage roots. They’re essential for explorers, indexers, MEV searchers, and analytics platforms. Due to massive storage requirements (e.g., Ethereum > 25 TB), they’re typically deployed on bare metal or high-performance environments.
---
## Bare Metal
Dedicated physical server hardware with no virtualization layer. Bare metal gives full control over compute, storage, and networking, offering low latency, predictable performance, and strong reliability. It's frequently used for validators, sequencers, RPC clusters, indexers, and MEV routers where every millisecond matters. Often combined with colocation for optimal network proximity.
---
## Block Storage
A storage architecture that divides data into fixed-size blocks, each with a unique identifier. Block storage provides raw, low-level storage that can be formatted with any file system and offers high performance with low latency — ideal for databases, virtual machines, and blockchain nodes requiring fast, random I/O access. Unlike object storage, block storage supports in-place modifications and is often used for archive nodes, indexers, and other stateful workloads where consistent disk performance is critical.
---
## Client
Software that connects to and interacts with a blockchain network.
- **Node Clients** (e.g., Geth) run the protocol, validate blocks, and maintain state.
- **Application Clients** (SDKs or libraries) let wallets, dApps, RPC endpoints, sequencers, and other systems communicate with nodes.
Clients define how networks achieve consensus and how external apps access blockchain state.
---
## Cluster
A group of interconnected nodes or servers that act as a single system to provide scalability, high availability, and performance. Clusters power RPC endpoints, validator sets, sequencers, and indexers. They enable horizontal scaling, automatic failover, geo-distribution, and centralized orchestration, forming the backbone of production-grade infrastructure.
---
## Colocation (Co-Lo)
Colocation is the practice of **placing your own physical servers inside professionally managed data centers** near major internet exchange points, chain hubs, or low-latency peering locations. Instead of relying on virtualized cloud infrastructure, you control the hardware, network configuration, and placement, while the facility provides power, cooling, security, and connectivity.
This setup gives teams deterministic network performance, minimal latency to peers, reduced egress costs, and hardware-level optimization.
*Example:* Hosting a Geth validator in a Tokyo Equinix TY2 data center to sit closer to Ethereum peers and propagation routes.
---
## Edge Computing
Edge computing is about **where and how workloads run**, not just where machines are located. It distributes software — such as RPC endpoints, indexers, caching layers, and sequencers — closer to users or data sources to reduce latency, improve redundancy, and optimize cost. It can run on co-lo hardware, cloud, or both.
*Example:* Deploying a caching RPC node in Singapore to serve Asia users while the main node remains in Tokyo.
*Nuance:* Co-lo = physical placement. Edge = workload distribution.
---
## Egress
The process of transferring data out of a cloud environment, often to another provider or the public internet. In Web3, egress is a major cost factor and can introduce latency and jitter. Teams reduce these issues through private interconnects or colocation, gaining more predictable network performance and avoiding hyperscaler egress fees.
---
## Full Node
A server that stores and validates the entire blockchain ledger from genesis. It maintains state, verifies transactions and blocks, and propagates data across the network. Full nodes provide the foundation for RPC services, explorers, sequencers, and DeFi apps, ensuring network security and data availability.
---
## Geth
Geth (*Go Ethereum*) is a **software client** and the most widely used implementation of Ethereum. It can run in full, light, or archive mode, exposing RPC and WebSocket APIs. Geth handles chain sync, transaction propagation, validation, and account management. It’s the reference implementation for Ethereum infra and is often deployed in containerized or bare metal setups.
---
## Hyperscaler
A hyperscaler is a **large-scale cloud service provider** that offers vast, elastic compute, storage, and networking resources globally. Examples include Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure. Hyperscalers provide flexibility and coverage but often come with trade-offs like unpredictable latency, noisy neighbors, and high egress costs — making them less ideal for deterministic Web3 infra compared to co-lo or edge setups.
---
## Ingestion
The entry point of the blockchain data pipeline. Ingestion involves pulling raw data — transactions, logs, events, and state updates — from nodes into processing systems. Efficient ingestion enables real-time indexing, analytics, and trading, especially for latency-sensitive workloads like MEV searchers, oracles, or cross-chain routers.
*Note:* Cloud providers often make ingestion **free or cheap** to attract workloads; the real cost typically comes from egress.
---
## Indexing
The process of organizing raw blockchain data into structured, queryable formats. Indexing powers explorers, dashboards, and analytics platforms by enabling fast data retrieval without rescanning the entire chain. A strong indexing layer improves performance and makes blockchain data usable for applications like sequencers and intent routers.
---
## Kubernetes (K8s)
Kubernetes is an open-source orchestration platform for managing containerized workloads. It’s widely used to run RPC clusters, validators, sequencers, and indexing services. Kubernetes automates rollouts, enables scaling, improves uptime, and standardizes infra operations across regions and chains.
---
## Light Node (Light Client)
A lightweight client that stores only minimal blockchain data (headers and proofs), fetching additional data from full nodes as needed. It’s ideal for mobile devices and other low-resource environments, allowing fast sync and broad network participation without storing the entire chain.
---
## Load Balancing
The process of distributing network traffic or workloads across multiple servers to avoid bottlenecks and ensure optimal performance. In Web3, load balancers improve RPC throughput, provide automatic failover, enable geo-routing, and help clusters scale reliably under high demand.
---
## Managed Service
A fully operated infrastructure offering provided by a third party. Managed services handle provisioning, scaling, upgrades, and monitoring for workloads like RPC endpoints, validator nodes, sequencers, and indexers. This lets teams focus on product instead of infrastructure, often backed by SLAs for reliability.
---
## NVMe
NVMe (*Non-Volatile Memory Express*) is a high-performance storage protocol designed for solid-state drives (SSDs) connected directly via PCIe. Unlike older protocols like SATA or SAS, NVMe offers significantly lower latency, higher throughput, and better parallelism — making it ideal for I/O-intensive workloads. In Web3, NVMe drives are essential for archive nodes, indexers, and validators that require fast random reads/writes and high IOPS to keep up with chain state and sync demands.
---
## RPC Node
A node that exposes RPC interfaces for applications to read blockchain data and broadcast transactions. RPC nodes power wallets, explorers, and protocols. They can run as full or archive nodes, and their latency, uptime, and capacity directly shape user experience.
---
## Virtualization
A computing method that abstracts physical hardware into multiple **virtual machines or containers**, allowing multiple workloads to share the same physical server. Virtualization enables flexible scaling and efficient resource allocation but can add latency and reduce determinism compared to bare metal. It’s widely used in cloud environments to deploy validators, sequencers, and RPC services at scale.
---
title: Welcome to Nirvana Labs
description: Explore guides and tutorials to start building on Nirvana Labs platform
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/index.md
---
import { Card, CardGrid } from '@astrojs/starlight/components';
import Footer from '../../components/footer.astro'
- [Set up AWS Direct Connect](/cloud/networking/connect/how-to/set-up-aws-direct-connect)
- Creating a VPC
- Creating a VM
- Creating a Volume
- Attaching/Detaching Volumes
- [Setup AI Tooling](/ai-tooling)
- [VMs](/cloud/compute/vms/)
- [Volumes](/cloud/compute/volumes)
- [Accelerated Block Storage (ABS)](/cloud/compute/volumes/storage-types/abs)
- [VPCs](/cloud/networking/vpcs)
- [Firewall Rules](/cloud/networking/vpcs/firewall-rules)
- [Connect](/cloud/networking/connect)
- [RPC Nodes](/blockchain/rpc-nodes/)
- [API](https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/api)
- [Typescript](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@nirvana-labs/nirvana)
- [Go](https://github.com/Nirvana-Labs/nirvana-go)
- [Terraform](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/nirvana-labs/nirvana/latest)
- [CLI](https://github.com/nirvana-labs/nirvana-cli)
- [MCP](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@nirvana-labs/nirvana-mcp)
---
title: SDKs & Tools
source_url:
html: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/sdks/
md: https://docs.nirvanalabs.io/sdks/index.md
---
import { Tabs, TabItem } from '@astrojs/starlight/components';
Nirvana Labs provides official SDKs, CLI tools, and infrastructure-as-code integrations to help you interact with the Nirvana API programmatically.
## Available SDKs
| SDK | Package | Repository |
|-----|---------|------------|
| TypeScript | [@nirvana-labs/nirvana](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@nirvana-labs/nirvana) | [GitHub](https://github.com/nirvana-labs/nirvana-typescript) |
| Go | [nirvana-go](https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/nirvana-labs/nirvana-go) | [GitHub](https://github.com/nirvana-labs/nirvana-go) |
## Infrastructure & Automation
| Tool | Package | Repository |
|------|---------|------------|
| Terraform | [nirvana-labs/nirvana](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/nirvana-labs/nirvana/latest) | [GitHub](https://github.com/nirvana-labs/terraform-provider-nirvana) |
| CLI | - | [GitHub](https://github.com/nirvana-labs/nirvana-cli) |
| MCP | [@nirvana-labs/nirvana-mcp](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@nirvana-labs/nirvana-mcp) | [GitHub](https://github.com/nirvana-labs/nirvana-typescript/tree/main/packages/mcp-server) |
## Examples
```hcl
# Declare the provider and version
terraform {
required_providers {
nirvana = {
source = "nirvana-labs/nirvana"
version = "~> 1.24.2"
}
}
}
# Initialize the provider
provider "nirvana" {
api_key = "My API Key" # or set NIRVANA_LABS_API_KEY env variable
}
# Configure a resource
resource "nirvana_compute_vm" "example_compute_vm" {
boot_volume = {
size = 100
type = "nvme"
tags = ["production", "ethereum"]
}
cpu_config = {
vcpu = 2
}
memory_config = {
size = 2
}
name = "my-vm"
os_image_name = "ubuntu-noble-2025-10-01"
public_ip_enabled = true
region = "us-wdc-1"
ssh_key = {
public_key = "ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIDBIASkmwNiLcdlW6927Zjt1Hf7Kw/PpEZ4Zm+wU9wn2"
}
subnet_id = "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000"
data_volumes = [{
name = "my-data-volume"
size = 100
type = "nvme"
tags = ["production", "ethereum"]
}]
tags = ["production", "ethereum"]
}
```
```bash
curl https://api.nirvanalabs.io/v1/compute/vms \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $NIRVANA_LABS_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"boot_volume": {
"size": 100,
"type": "nvme"
},
"cpu_config": {
"vcpu": 2
},
"memory_config": {
"size": 2
},
"name": "my-vm",
"os_image_name": "ubuntu-noble-2025-10-01",
"public_ip_enabled": true,
"region": "us-wdc-1",
"ssh_key": {
"public_key": "ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIDBIASkmwNiLcdlW6927Zjt1Hf7Kw/PpEZ4Zm+wU9wn2"
},
"subnet_id": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"tags": [
"production",
"ethereum"
]
}'
```
```go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/nirvana-labs/nirvana-go"
"github.com/nirvana-labs/nirvana-go/compute"
"github.com/nirvana-labs/nirvana-go/option"
"github.com/nirvana-labs/nirvana-go/shared"
)
func main() {
client := nirvana.NewClient(
option.WithAPIKey("My API Key"), // defaults to os.LookupEnv("NIRVANA_LABS_API_KEY")
)
operation, err := client.Compute.VMs.New(context.TODO(), compute.VMNewParams{
BootVolume: compute.VMNewParamsBootVolume{
Size: 100,
Type: compute.VolumeTypeNvme,
},
CPUConfig: compute.CPUConfigRequestParam{
Vcpu: 2,
},
MemoryConfig: compute.MemoryConfigRequestParam{
Size: 2,
},
Name: "my-vm",
OSImageName: "ubuntu-noble-2025-10-01",
PublicIPEnabled: true,
Region: shared.RegionNameUsWdc1,
SSHKey: compute.SSHKeyRequestParam{
PublicKey: "ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIDBIASkmwNiLcdlW6927Zjt1Hf7Kw/PpEZ4Zm+wU9wn2",
},
SubnetID: "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
})
if err != nil {
panic(err.Error())
}
fmt.Printf("%+v\n", operation.ID)
}
```
```typescript
import NirvanaLabs from '@nirvana-labs/nirvana';
const client = new NirvanaLabs({
apiKey: process.env['NIRVANA_LABS_API_KEY'], // This is the default and can be omitted
});
const operation = await client.compute.vms.create({
boot_volume: { size: 100, type: 'nvme' },
cpu_config: { vcpu: 2 },
memory_config: { size: 2 },
name: 'my-vm',
os_image_name: 'ubuntu-noble-2025-10-01',
public_ip_enabled: true,
region: 'us-wdc-1',
ssh_key: {
public_key: 'ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIDBIASkmwNiLcdlW6927Zjt1Hf7Kw/PpEZ4Zm+wU9wn2',
},
subnet_id: '123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000',
});
console.log(operation.id);
```
```bash
nirvana compute:vms create \
--name my-vm \
--region us-wdc-1 \
--boot-volume '{"size": 100, "type": "nvme"}' \
--cpu-config '{"vcpu": 2}' \
--memory-config '{"size": 2}' \
--os-image-name ubuntu-24.04 \
--public-ip-enabled true \
--subnet-id subnet-uuid \
--ssh-key '{"public_key": "ssh-ed25519 AAAA..."}'
```